- StemEdit Gene Editing Services
- StemEdit Case Studies
Case Study in AI-Designed Gene Editing
Ready-to-use StemEdit Hypoimmune Lines:
What’s New
Optimized for Reduced Immunogenicity and Allogeneic Compatibility
REPROCELL’s StemEdit Hypoimmune iPSC lines will be immediately available, can be evaluated under research conditions, and allow you to easily progress to clinical translation. Built on one of our StemRNA™ Clinical iPSC Seed Clones, these lines are generated using our proprietary genome editing system and reprogrammed with footprint-free StemRNA™ technology under GMP principles.
Hypoimmune StemEdit Lines
- HLA Class I/II Double Knockout
StemEdit Human iPSC non-HLA Class I/II (B2M/CIITA Homo Double KO) - HLA Class I Knockout
StemEdit Human iPSC non-HLA Class I (B2M Homo KO) - HLA Class II Knockout
StemEdit Human iPSC non-HLA Class II (CIITA Homo KO)
We also offer GMP iPSC Master Cell Bank (MCB) vials derived from the parental iPSC line as an affordable starting point for your own clinical gene editing projects and custom Hypoimmune line generation.
For detailed specifications, pricing, or to discuss your project needs, contact us at info-us@reprocell.com.
Key Benefits
- Standardized, well-characterized genetic modifications
- Immediate availability for research programs
- Clear pathway to matched clinical-grade seed clones
- GMP-aligned development and traceability
- Ready for both research use and clinical translation
Our off-the-shelf lines provide speed for your research program without closing the door on future clinical development.
Outline: Modulation of Immune Response by Editing HLA Class I and Class II
One limitation of using iPSCs clinically is immunogenicity caused by Human Leucocyte Antigen (HLA) mismatching, which can reduce the in vivo survival and therapeutic efficacy of these cells.1,2 The immunogenicity of iPSCs can be reduced by disrupting the genes responsible for immune recognition using StemEdit's advanced gene editing platform. One approach is to knock-out the B2M (β2 microglobulin) and CIITA (major histocompatibility complex [MHC] II transactivator) genes, creating the basis for the generation of hypoimmune cell lines.
In humans, the B2M protein is required for the presentation of HLA protein A-G on the cell surface, while CIITA is essential for HLA-II transcription.2,3 Dual knock-out of the B2M and CIITA genes disrupts the presentation of MHC-I/MHC-II proteins in iPSCs, improving their therapeutic potential while maintaining pluripotency.1
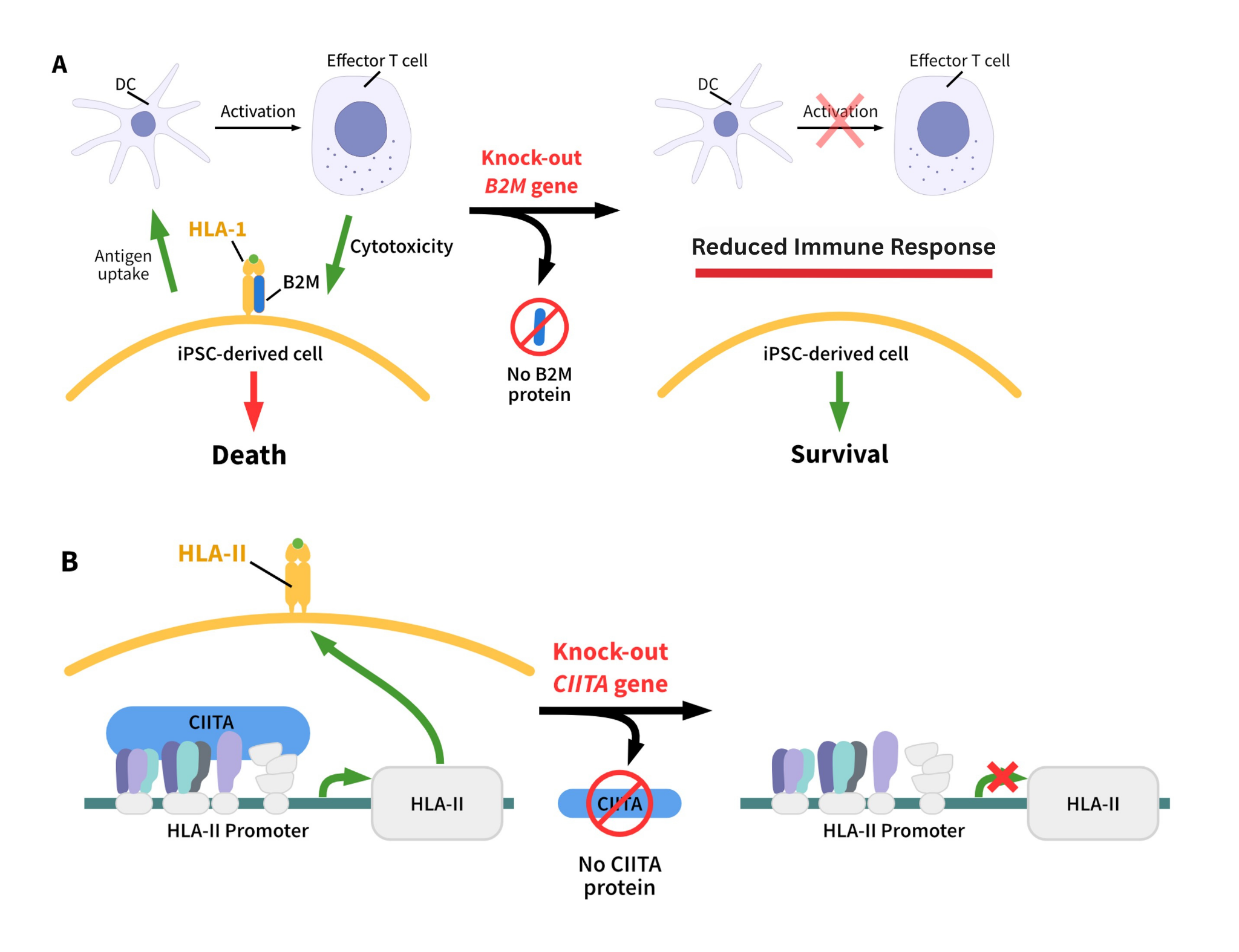
Role of B2M and CIITA in the regulation of the immune response. B2M regulates the activation of effector T cells. B2M knockouts do not activate effector T cells, leading to a reduced immune response. CIITA regulates the expression of the HLA-II complex. Knockout of CIITA leads to a reduced expression of HLA-II, and a reduced immune response.
References
- Wang X et al. Diminished expression of major histocompatibility complex facilitates the use of human induced pluripotent stem cells in monkey. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 11:334 (2020).
- Xu H et al. Targeted Disruption of HLA Genes via CRISPR-Cas9 Generates iPSCs with Enhanced Immune Compatibility. Cell Stem Cell 24 pp566-578 (2019).
- Deuse et al. Hypoimmunogenic derivatives of induced pluripotent stem cells evade immune rejection in fully immunocompetent allogeneic recipients. Nature Biotechnology 37 pp 252–258 (2019).
Case Study: Hypoimmune iPSC Generation
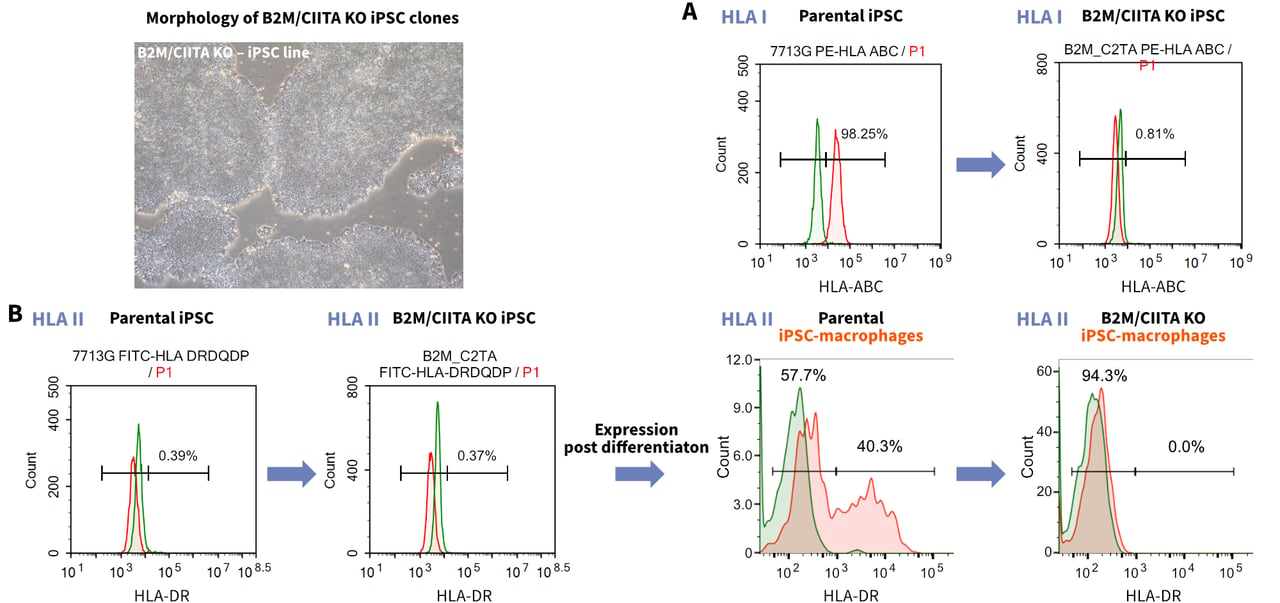
HLA Class I and II expression in B2M/CIITA double knock-out iPSCs. HLA expression was measured by flow cytometry in the unedited parental iPSC line and after knock-out of the B2M and CIITA genes. Expression of HLA I and II is suppressed in B2M/CIITA knockout lines. Results indicate that the generation of iPSC for the purpose of suppressing an immune rejection is successful with StemEdit.
(A.) HLA Class I expression was measured in the parental iPSC-derived macrophages by flow cytometry.
(B.) Undifferentiated iPSCs (“Parental iPSCs”) do not express HLA II. Expression of HLA Class II occurs only in cells post differentiation. Expression of the HLA II gene HLA-DR was therefore measured in iPSC-derived macrophages.
Contact our experts
Discover more
Gene Editing Services
- GMP iPSC Production Service
- GMP iMSC & MSC Production Service
- iPSC-Derived Exosome Production Service
- GMP iPSC/iMSC MCB Manufacturing – REPROCELL USA
- GMP iPSC/MSC MCB Manufacturing – Histocell (Europe Partner Overview)
- REPROCELL Japan GMP Manufacturing Facility
- For clinical use: Ready-to-use GMP MSCs
Resources
- FAQ: Clinical iPSCs
- FAQ: Clinical MSCs
- FAQ: iPSC-Derived Exosomes
- Making iPSC-Derived Therapeutics a Clinical Reality – our external article in the European Biopharmaceutical Review.
On the REPROCELL blog
Latest in Gene Editing

OpenCRISPR-1: The First AI-Designed CRISPR Editor for High-Precision Gene & Cell Therapy
Discover OpenCRISPR-1 — the first fully AI-designed CRISPR–Cas editor. Built by generative large language model, it enables high-efficiency, high-specificity genome and base editing in human cells. Ideal for cell therapy, stem-cell research, and advanced gene-editing workflows.
16 December 2025

Key Challenges in Clinical iPSC Applications: How REPROCELL Helps You Succeed
Overcome key challenges in clinical iPSC applications with REPROCELL's ethical sourcing, advanced reprogramming, and tailored solutions for reliable, scalable therapies.
12 May 2025

The Therapeutic Advantage of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (iMSCs)
Discover the clinical benefits and advancements of using induced pluripotent stem cells-derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMSCs) in regenerative medicine and therapeutic applications.
24 February 2025
