Bronchoconstriction in denuded secondary healthy human airways (Muscarinic receptor)
Drug Discovery Assay – reference number: B060
Overview
| Assay type: | Respiratory |
| Tissue: | Human secondary airways (healthy – denuded) |
| Target: | Muscarinic receptor |
| Control compound: | Carbachol |
| Study type: | Organ bath |
| Functional endpoint: | Bronchoconstriction |
Assay Description
This assay assesses whether test compounds cause bronchoconstriction in denuded human airways with carbachol as a reference compound.
The airways of the respiratory tract offer resistance to the flow of air during inhalation and expiration. Any alterations to the airways (for example contractile state, increased mucus or inflammation of the airways) can affect airflow and gas exchange.
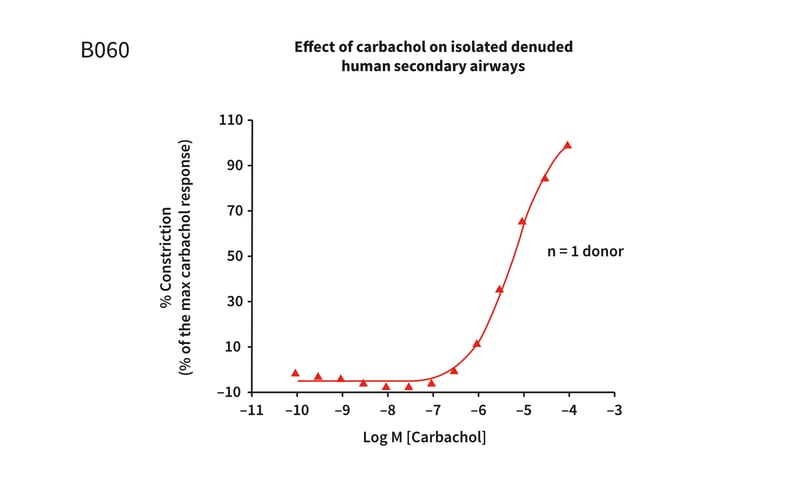 Figure 1: Cumulative concentration response curve to carbachol, incubated with 10µM propanolol, in isolated denuded human airways, demonstrating concentration dependent contraction response. The Log EC50= −5.27 ± 0.04M (5.4µM) (mean ± S.E.M), with a maximum contractile response of 100 ± 10.7% at 1x10−4M.
Figure 1: Cumulative concentration response curve to carbachol, incubated with 10µM propanolol, in isolated denuded human airways, demonstrating concentration dependent contraction response. The Log EC50= −5.27 ± 0.04M (5.4µM) (mean ± S.E.M), with a maximum contractile response of 100 ± 10.7% at 1x10−4M.
Testing Information
Introduction
The specific results that will be provided are the effects of increasing concentrations of test articles on the contractile state of isolated denuded human airways.
Test Article Requirements
Test article(s) to be provided by the Sponsor in storable aliquots at required test concentrations with information on diluent vehicle used. Stock solutions are prepared in distilled water unless otherwise requested. Bath volumes are 5mL; sponsor to provide sufficient test article to run the entire study.
Suggested Testing
In duplicate at 6 concentrations.
Study Outline
Rationale and Experimental Design
This assay assesses whether test compounds cause bronchoconstriction in denuded human airways with carbachol as a reference compound.
Exclusion Criteria
No specific exclusion criteria are in place other than to reject macroscopically diseased/necrotic tissue. Furthermore, tissues which do not respond to the standard pharmacology checks will be excluded.
Standardisation and Qualification
All individual airways are initially processed through standardisation and qualification procedures to ensure functionality, prior to starting the study protocol.
Airways are processed through a standardisation procedure to reduce signal variability prior to pharmacological intervention. This ensures that airways are maintained under appropriate physiological tension throughout the experiments.
Following standardisation, the airways are challenged with an appropriate bronchoconstrictive agent to ensure robust contractile responses.
Test tissues are then washed, and the responses allowed to return to baseline.
Airways which pass the standardisation and qualification pass/fail criteria will then progress to the study protocol.
Bronchoconstriction Assays
Agonist Bronchoconstriction Assays
To assess their ability to elicit bronchoconstriction, 6 point cumulative concentration response curves will be performed for each test article. These concentration response curves (CCRC’s) will be performed from resting baseline tension. A positive control compound and representative test article vehicle CCRC will also be run to allow direct comparison with test articles.
An example of the conditions assessed for 3 test articles are detailed below (each condition will be run in duplicate airways):
-
Representative test article vehicle CCRC
-
Positive control CCRC
-
Test article 1 CCRC
-
Test article 2 CCRC
-
Test article 3 CCRC
Supplementary Option
To assess the involvement of a specific receptor subtype in any observed responses, the concentration of test article eliciting the largest response can subsequently (following a wash out and recovery period) be tested in the presence of a specific antagonist. This supplementary option will incur an extra charge.
Antagonist Bronchoconstriction Assays
Option 1 − IC50 Determination
To assess the ability of each test article to antagonise an agonist mediated bronchoconstriction response, 6 point cumulative concentration response curves (CCRC’s) will be performed for each test article. These CCRC’s will be performed following pre-constriction with an appropriate bronchoconstrictive reference agonist. A positive control compound and representative test article vehicle CCRC will also be run to allow direct comparison with test articles.
An example of the conditions assessed for 3 test articles are detailed below (each condition will be run in duplicate airways):
-
Representative test article vehicle CCRC
-
Test article 1 CCRC
-
Test article 2 CCRC
-
Test article 3 CCRC
-
Positive control CCRC
Option 2 − pA2 Determination
To assess the ability of a test article to antagonise an agonist mediated bronchoconstriction response; 6 point cumulative concentration response curves (CCRC’s) will firstly be performed for the bronchoconstrictive reference agonist. Following a wash out and recovery period, airways will be incubated with the test article (3 different concentrations of test article will be assessed), positive control or test article vehicle before the same 6 point cumulative concentration response curve will be repeated for the reference agonist.
An example of the conditions assessed for 3 test articles are detailed below (each condition will be run in duplicate airways):
-
Representative test article vehicle
-
Test article 1 concentration 1
-
Test article 1 concentration 2
-
Test article 1 concentration 3
-
Test article 2 concentration 1
-
Test article 2 concentration 2
-
Test article 2 concentration 3
-
Test article 3 concentration 1
-
Test article 3 concentration 2
-
Test article 3 concentration 3
-
Positive control
Analysis
Responses shall be expressed either in milligrams or grams tension, or as a % of the maximal contractile response (e.g. KPSS). Statistical analysis (where appropriate) will be performed using GraphPad Prism, with the results being shown in graphical form in the final report.


.jpg?width=756&height=425&name=Untitled%20design%20(5).jpg)