Recombinant human FGF-19 protein
QK086
Brand: Qkine
Fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF-19), a member of the FGF family, and plays a role in regulating metabolic processes. FGF-19 is expressed by embryonic stem cells and can be used in stem cell and organoid cultures to promote liver and osteogenic differentiation.
FGF-19 is a high purity protein with a molecular weight of 21.8 kDa. This protein is animal origin-free, carrier-free and tag-free to ensure its purity with exceptional lot-to-lot consistency. Qkine FGF-19 is suitable for the culture of reproducible and high-quality stem cells, primary cells and organoids.

Currency:
| Product name | Catalog number | Pack size | Price | Price (USD) | Price (GBP) | Price (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant human FGF-19 protein, 25 µg | QK086-0025 | 25 µg | (select above) | $ 260.00 | £ 190.00 | € 222.00 |
| Recombinant human FGF-19 protein, 50 µg | QK086-0050 | 50 µg | (select above) | $ 380.00 | £ 280.00 | € 320.00 |
| Recombinant human FGF-19 protein, 100 µg | QK086-0100 | 100 µg | (select above) | $ 560.00 | £ 410.00 | € 479.00 |
| Recombinant human FGF-19 protein, 500 µg | QK086-0500 | 500 µg | (select above) | $ 2225.00 | £ 1625.00 | € 1898.00 |
| Recombinant human FGF-19 protein, 1000 µg | QK086-1000 | 1000 µg | (select above) | $ 3465.00 | £ 2530.00 | € 2956.00 |
Note: prices shown do not include shipping and handling charges.
Qkine company name and logo are the property of Qkine Ltd. UK.
Alternative protein names
Species reactivity
- human
- species similarity:
- mouse - 51%
- rat - 52%
- bovine - 75%
- porcine - 77%
Summary
- High purity human FGF-19 (UniProt: O95750)
- 21.8 kDa (monomer)
- >98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
- Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
- Expressed in E. coli
- Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
- Lyophilized from PBS, mannitol
- Resuspend in sterile-filtered water at >50 µg/ml, add carrier protein if desired, prepare single use aliquots and store frozen at -20 °C (short-term) or -80 °C (long-term).
Featured applications
- Metabolic disease research
- Liver cell regeneration
- Cancer research including gastrointestinal cancers
- Directed osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
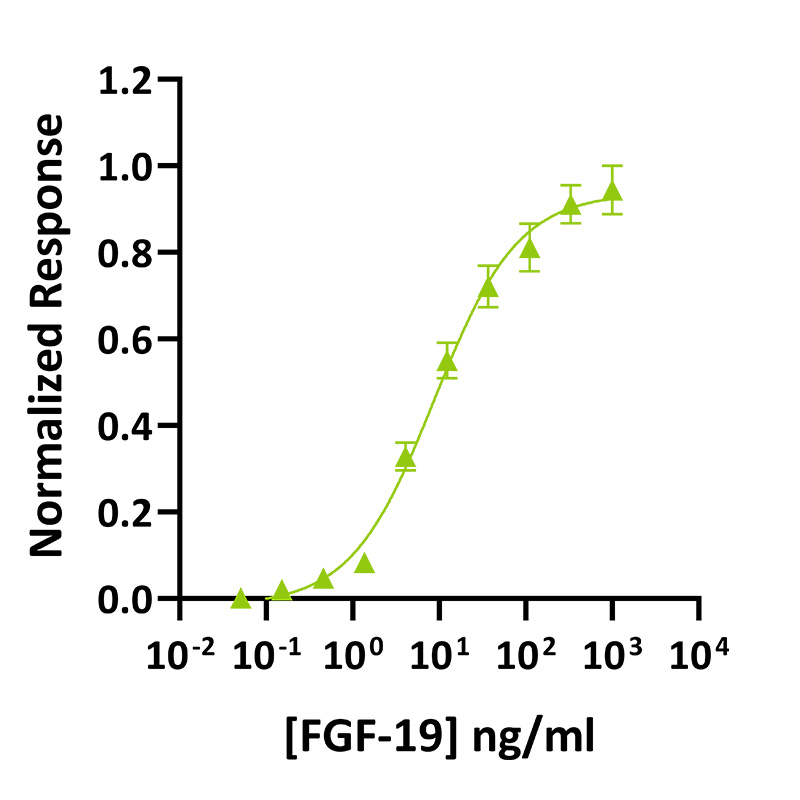
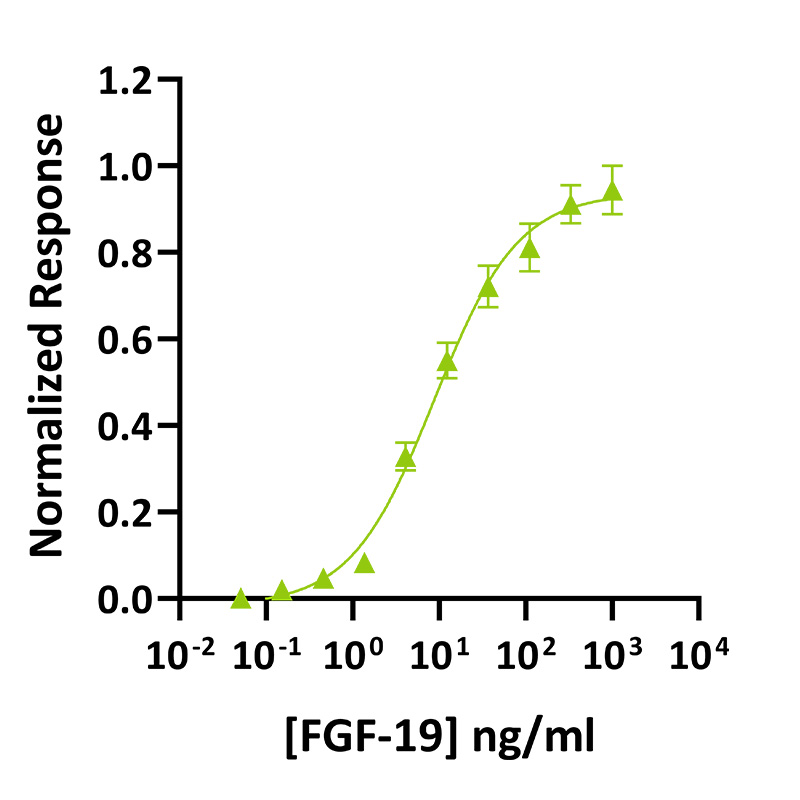
Bioactivity
Recombinant FGF-19 activity was determined using a FGF-19-responsive firefly luciferase reporter assay. Transfected HEK293T cells were treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of FGF-19 for 3 hours. Firefly activity was measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity. Data from Qk086 lot #204724. EC50 = 8.9 ng/ml (0.41 nM).
Purity
Recombinant FGF-19 migrates as a major band at approximately 25 kDa (monomer) in reduced (R) and at approximately 22 kDa in non-reduced (NR) conditions. No contaminating protein bands are present. The purified recombinant protein 3 µg was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptoethanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk086 lot #204724.
Further quality assays
- Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
- Recovery from stock vial: >95%
- Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
Protein background
Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 (FGF-19) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family and plays a significant role in regulating metabolic processes, especially in bile acid homeostasis, glucose metabolism, and lipid regulation [1-2].
FGF-19 is a 25 kDa protein primarily produced in the ileum of the small intestine in response to bile acids during digestion. Once secreted, FGF-19 acts by binding to the FGFR4 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4) and beta-Klotho co-receptor in target tissues like the liver [1].
FGF-19 consists of a core structure that shares commonality with other FGFs, including a beta-trefoil fold formed by anti-parallel beta-sheets. This structure is key to its interaction with FGFRs and beta-Klotho, which enhances its specificity for metabolic functions rather than cell proliferation, which is more characteristic of other FGFs. FGF-19 lacks the conventional heparin-binding domain seen in other FGFs, contributing to its endocrine-like action, allowing it to circulate and act distally from its site of production [3].
FGF-19 is widely studied for its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in metabolic diseases. In obesity and type 2 diabetes, FGF-19 helps regulate glucose levels by reducing hepatic glucose production and enhancing insulin sensitivity. Its role in cholesterol metabolism makes it a candidate for treating conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and primary bile acid disorders [2,4].
FGF-19 is used in studies focused on metabolic syndrome, liver diseases, and cancer. Researchers are exploring its ability to improve liver function and reduce inflammation in conditions like cirrhosis and NAFLD [4].
Background references
-
Mohammadi, M. et al. Structural basis for fibroblast growth factor receptor activation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 107–137 (2005). doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.01.008.
-
Xie, M.-H. et al. FGF-19, a novel fibroblast growth factor with unique specificity for FGFR4. Cytokine 11, 729–735 (1999). doi.org/10.1006/cyto.1999.0485.
-
Zhang, X. et al. FGF19 genetic amplification as a potential therapeutic target in lung squamous cell carcinomas. Thorac. Cancer 8, 655–665 (2017). doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12504.
-
Desnoyers, L. R. et al. Targeting FGF19 inhibits tumor growth in colon cancer xenograft and FGF19 transgenic hepatocellular carcinoma models. Oncogene 27, 85–97 (2008). doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210623.
FAQ
What is Fibroblast Growth Factor 19?
FGF-19 is a metabolic growth factor that regulates bile acid synthesis, glucose metabolism, and promotes liver regeneratio
Where is FGF-19 found?
FGF-19 is primarily found in the ileum, where it is produced in response to bile acids. It also acts on the liver, influencing metabolic processes such as bile acid regulation and glucose metabolism.
Is FGF-19 a cytokine?
No, FGF-19 is not classified as a cytokine. It is a growth factor, specifically part of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family.
What does the FGF-19 gene do?
The FGF-19 gene encodes the fibroblast growth factor 19 protein, which plays a key role in regulating various metabolic processes.
What does FGF-19 bind to?
FGF-19 binds to FGFR4 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4) as its primary receptor. For this interaction to occur effectively, FGF-19 also requires the presence of the co-receptor β-Klotho.
What is the FGF-19 signaling pathway?
The FGF-19 pathway is activated when FGF-19 binds to FGFR4 and β-Klotho, triggering MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling.
How is FGF-19 used in cell culture?
FGF-19 is used in cell culture to promote hepatocyte growth, study metabolic processes, support stem cell differentiation into liver-like cells, aid tissue engineering, and investigate its role in cancer research, enhancing understanding of cellular responses and therapeutic potential.