Stemolecule™ A83-01
04-0014 / 04-0014-10
Brand: Stemolecule™
A83-01 is a selective inhibitor of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) type I receptor ALK5, the Activin/Nodal receptor ALK4, and the nodal receptor ALK71.
- A-83-01
- A 83-01
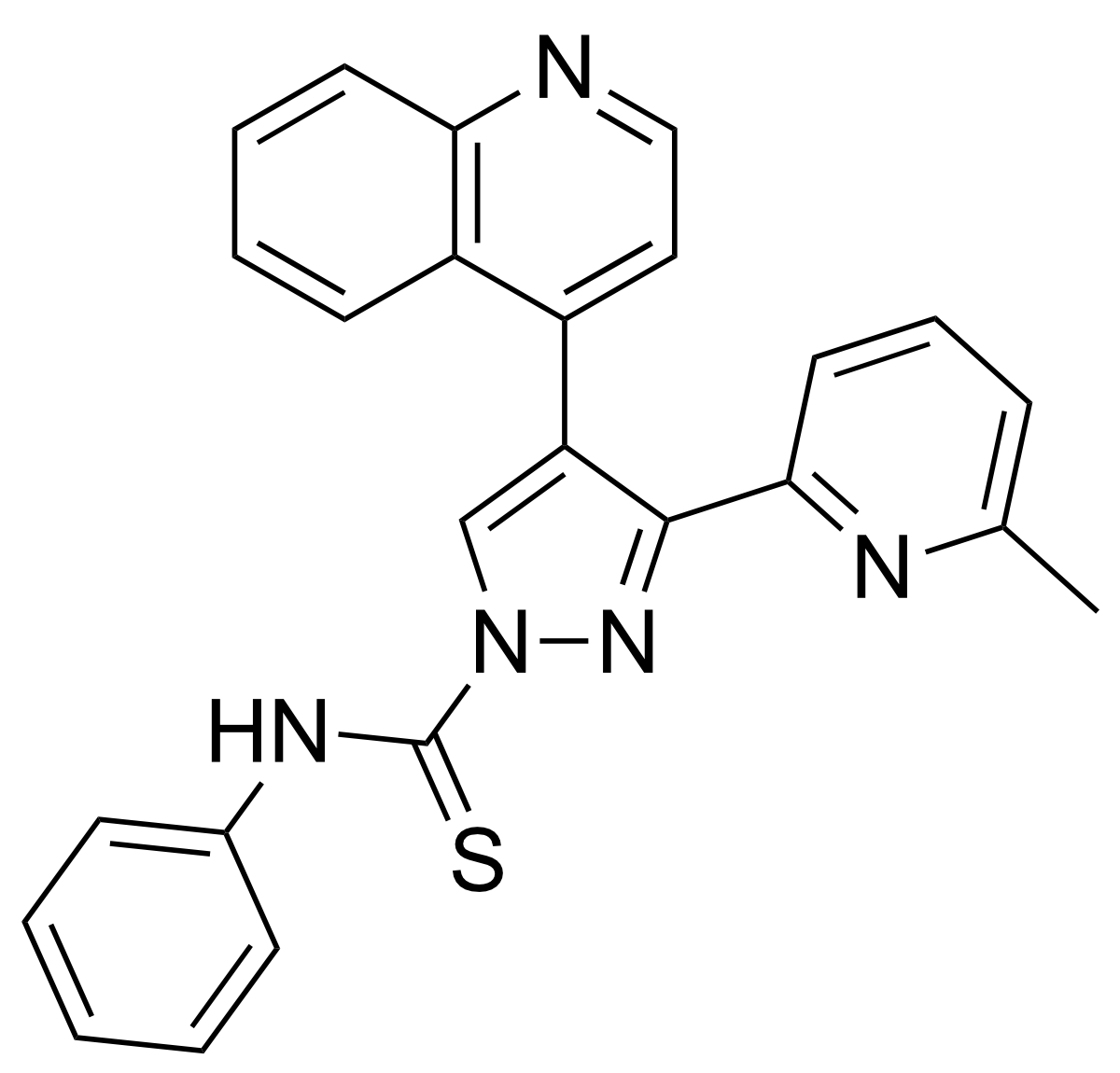
- 3-(6-Methyl-2-pyridinyl)-N-phenyl-4-(4-quinolinyl)-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide
Currency:
| Product name | Catalog number | Pack size | Price | Price (USD) | Price (GBP) | Price (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stemolecule™ A83-01 (2 mg) | 04-0014 | 2 mg | (select above) | $ 162.00 | £ 133.00 | € 156.00 |
| Stemolecule™ A83-01 (10 mg) | 04-0014-10 | 10 mg | (select above) | $ 541.00 | £ 442.00 | € 517.00 |
Note: prices shown do not include shipping and handling charges.
Product Information
A83-01 is a selective inhibitor of the transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) type I receptor ALK5, the Activin/Nodal receptor ALK4, and the nodal receptor ALK71. This molecule is more potent than SB431542 in its inhibition of ALK4, 5, and 7, and only weakly inhibits ALK1, 2, 3, and 6. A83-01 inhibits the TGFβ-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via the inhibition of Smad2 phosphorylation2.

Stemgent and the Stemolecule brand name are trademarks of REPROCELL Inc., Japan.
Product Name: Stemolecule A83-01
Catalog Number: 04-0014
Pack Size:
- 2 mg (Cat. No. 04-0014)
- 10 mg (Cat. No. 04-0014-10)
Alternate Name(s):
- A-83-01
- A 83-01
- 3-(6-Methyl-2-pyridinyl)-N-phenyl-4-(4-quinolinyl)-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide
Chemical Formula: C25H19N5S
Molecular Weight: 421.52
CAS Number: 909910-43-6
Purity: Greater than 98% by HPLC analysis
Formulation: Pale yellow solid
Solubility: A83-01 is soluble in DMSO at 50 mM.
Storage and Stability: Store powder at 4 °C protected from light. Information about the stability of Stemolecules in solution is largely not available. As a general guideline, we recommend that stock solution be freshly made and stored in aliquots at −20 °C. The effect of storage of stock solutions should be verified for each application.
Quality Control: The purity of A83-01 was determined by HPLC analysis. The accurate mass was determined by mass spectrometry. No acute cytotoxicity was observed in mouse embryonic stem cells following a 6 hour exposure to 1 nM - 100 µM A83-01.
Specification Sheets:
Safety Data Sheets:
- Tojo, M., Hamashima, Y., Hanyu, A., Kajimoto, T., Saitoh, M., Miyazono, K., Node, M., and Imamura, T. The ALK-5 inhibitor A-83-01 inhibits Smad signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by transforming growth factorβ. Cancer Sci 96: 791-800 (2005).
- Li, W., Wei, W., Zhu, S., Zhu, J., Shi, Y., Lin, T., Hao, E., Hayek, A., Deng, H., and Ding, S. Generation of rat and human induced pluripotent stem cells by combining genetic reprogramming and chemical inhibitors. Cell Stem Cell 4: 16-19 (2009).
Additional Publications
- Ai Z; Xiang X; Xiang Y; Szczerbinska I; Qian Y; Xu X; Ma C; Su Y; Gao B; Shen H; bin Ramli MN; Chen D; Liu Y; Hao J-j; Ng HH; Zhang D; Chan Y-S; Liu W; Liang H. Krüppel-like factor 5 rewires NANOG regulatory network to activate human naive pluripotency specific LTR7Ys and promote naive pluripotency. Cell Reports 40:111240 (2022).
- Tsukamoto M; Kimura K; Yoshida T; Sugiura K; Hatoya S. Canine induced pluripotent stem cells efficiently differentiate into definitive endoderm in 3D cell culture conditions using high-dose activin A. Regen Therapy 21:502 (2022).
- Weiß F; Holthaus D; Kraft M; Klotz C; Schneemann M; Schulzke JD; Krug SM. Human duodenal organoid-derived monolayers serve as a suitable barrier model for duodenal tissue. Ann New York Acad Sci 1515:155 (2022).
- Mao Z; Li Y; Huang L; Chen Y; Luo H; Zhang S; Chen H; . Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line HUSTTJi001-A from a Moyamoya disease patient with RNF213 gene mutation. Stem Cell Res 57:102575 (2021).
- Kimura K; Tsukamoto M; Tanaka M; Kuwamura M; Ohtaka M; Nishimura K; Nakanishi M; Sugiura K; Hatoya S. Efficient Reprogramming of Canine Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells into Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Develop in press:https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2020.0084 (2020).
- Wang T; Li J; Xiao Y; Fu B; Wang P; Bai X; Cai G; Chen X; Li Q. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cell PLAFMCi002-A derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of polycystic kidney disease patient with PKD1 mutation. Stem Cell Res 49:102039 (2020).
- Wang S-H; Wang X-P. Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line (THSJTUi001-A) from a Wilson's disease patient harboring a homozygous Arg778Leu mutation in ATP7B gene. Stem Cell Res 49:102050 (2020).
- Liu WM; Cheng RR; Niu ZR; Chen AC; Ma MY; Li T; Chiu PC; Pang RT; Lee YL; Ou JP ; Yao YQ; Yeung WSB. Let-7 derived from endometrial extracellular vesicles is an important inducer of embryonic diapause in mice. Sci Adv 6:eaaz7070 (2020).
- Shan H; Ye J; Zhuang T; TIanRui H; HaiPing X; ShengSheng Z; XinYue H; HanYu L; Lun W; ShuYang Z. Establishment of an induced pluripotent stem cell line PUMCHi004-A from a hereditary transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy patient with transthyretin (TTR) p.Asp38Asn mutation. Stem Cell Res :102022 (2020).
- Shen H; Ye J; Ping XH; Yue HX; Yang ZS. Establishment of an induced pluripotent stem cell line from a patient with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis carrying transthyretin (TTR) mutation p.Phe53Val. Stem Cell Res https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2020.101940: (2020).
- Long P; Liu Z; Wu B; Chen J; Sun C; Wang F; Huang Y; Chen H; Li Q; Ma Y. Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line from chorionic villi of a Patau syndrome spontaneous abortion. Stem Cell Res 45:101789 (2020).
- Ghatak S; Dolatabadi N; Trudler D; Zhang XT; Wu Y; Mohata M; Ambasudhan R; Talantova M; Lipton SA. Mechanisms of hyperexcitability in Alzheimer's disease hiPSC-derived neurons and cerebral organoids vs. isogenic control. eLife 8:e50333 (2019).
- Vahdat S; Pahlavan S' Mahmoudi E; Barekat M; Ansari H; Bakhshandeh B; Aghdami N; Baharvand H. Expansion of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Early Cardiovascular Progenitor Cells by a Cocktail of Signaling Factors. Sci Rep 9:16006 (2019).
- Peng L; Zhou Y; Xu W; Jiang M; Li H; Long M; Liu W; Liu J; Zhao X; Xiao Y. Generation of Stable Induced Pluripotent Stem-like Cells from Adult Zebra Fish Fibroblasts. Int J Biol Sci 15:2340 (2019).
- Harmanto Y; Maki T; Yakagi Y; Miyamoto S; Takahashi J. Xeno‐free culture for generation of forebrain oligodendrocyte precursor cells from human pluripotent stem cells. J Neuro Res 2019:1-18 (2019).
- Wang L; De SOlis AJ; Goffer Y; Birkenback KE; Engle SE; Tanis R; Levenson JM; Lu X; Rausch R: Purohit M; Lee J-Y; Tan J; De Rosa MC; DOege CA; Aaron HL; Martins G; Brüning JC; Egli D; Costa R; Berbari N; Leibel RL; Stratigopoulos G. Ciliary gene RPGRIP1L is required for hypothalamic arcuate neuron development. JCI Insight 4:e123337 (2019).
- Guo Y; Lei I; Tian S; Gao W; Hacer K; Li Y; Wang S; Liu L; Wang Z. Enhancing Cardiac Reprogramming by Suppressing Specific C-C Chemokine Signaling Pathways. bioRxiv :http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/522995 (2019).
- Peng Q; Yue C; Chen ACH; Lee KC; Fong SW; Yueng WSB; Lee YL. Connexin 43 is involved in early differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Differentiation 105:33-44 (2019).
- Whitworth DJ; Limnios IJ; Gauthier M-E; Weeratunga P; Ovchinnikov DA; Baillie G; Grimmond SM; Graves JAM; Wolvetang EJ. Platypus Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: the Unique Pluripotency Signature of a Monotreme . BioRXiv 43306: (2018)
- Wang X; Sterr M; Burtscher I; CHen S; Hieronimus A; Machicao F; Staiger H; Haring H-U; Lederer G; Irmler M; Bechers J; de Angelis MH; Ray M; Wright CVE; Bakhti M; Lickert H. Genome-wide analysis of PDX1 target genes in human pancreatic progenitors. Mol Metab 9:57-68 (2018).
- Han Y-C, Lim Y; Duffieldl MD; Liu J; Manaph NPA; Yang M; Keating DJ; Zhou X-F. Direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts to neural stem cells by small molecules. Stem Cells International 2016:4304916 (2016).
- Zhu S; Russ HA; Wang X; Zhang M; Ma T; Xu T; Tang S; Hebrok M; Deng S. Human pancreatic β-like cells converted from fibroblasts. Nature Commun 7:10080 (2016).
- Zhu S; Wang H; Deng S. Reprogramming fibroblasts toward cardiomyocytes, neural stem cells and hepatocytes by cell activation and signaling-directed lineage conversion. Nature Protocols 10, 959-973 (2015).
- Liu G. No detection of potential cancer risk for free-viral reprogrammed stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons from adult mice fibroblasts. J Stem Cell Res Ther 5:286 (2015).
- Lee Y-L; Fong S-W; Chen ACH; Li T; Yue C; Lee C-L; Ng ENY; Yueng WSB; Lee K-F. Establishment of a novel human embryonic stem cell-derived trophoblastic spheroid implantation model. Hum Reprod 30:2614 (2015).
- Higuchi S; Watanabe TM; Kawauchi K; Ichimura T; Fujita H. Culturing of mouse and human cells on soft substrates promot the expression of stem cell markers. J Biosci Bioeng 117:749 (2014).
- Manoli DS; Subramanyam D; Carey C; Sudin E; Van Westerhuyzen J A; Bales KL; Belloch R; Shah NM. Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from the Prairie Vole. PLoS One 7(5): e38119 (2012).
- Nagy, K., Sung, H-K., Zhang, P., Laflamme, S., Vincent, P, Agha-Mohammadi, S., Woltjen, K., Monetti, C., Michael, I. P., Smith, L. C., Nagy, A. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines Derive from Equine Fibroblasts. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports 7:693 (2011).
- Mack, A., Kroboth, S., Rajesh, D., Wang, W. B. Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from CD34+ Cells across Blood Drawn from Multiple Donors with Non-Integrating Episomal Vectors. PLoS One 6(11): e27956.(2011).