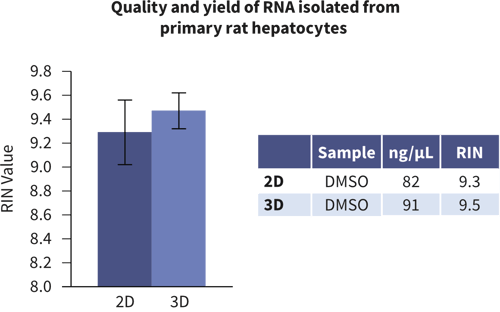
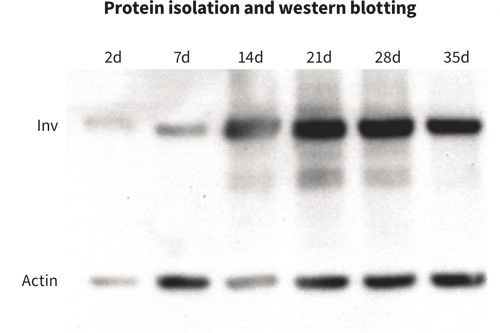
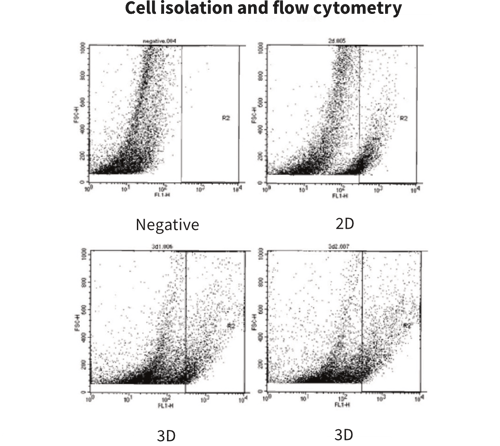
Alvetex compatibility with biology techniques
Alvetex is compatible with a wide range of cell biology techniques. Following are some examples.
Imaging
Imaging reveals the integrity of in vivo-like structure and organization.
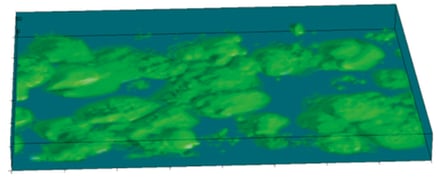
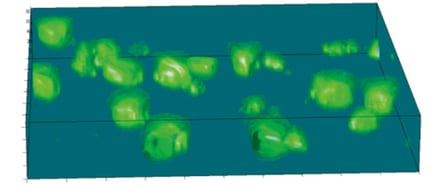
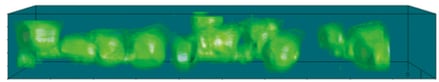
Changes in cellular morphology and function limit the value of cells grown in 2D cell culture. 3D culture systems enable cells to form more complex structures. Various models have been developed to create 3D skin constructs in vitro, including raft cultures. These methods are often technically challenging, involve multiple steps, show poor reproducibility and are difficult to practice routinely.
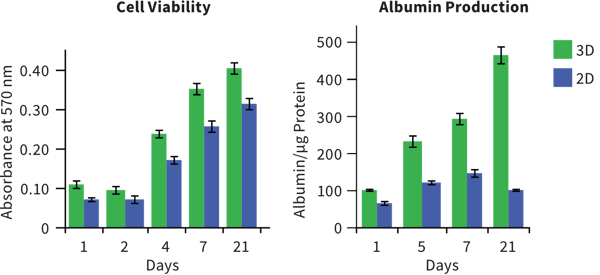
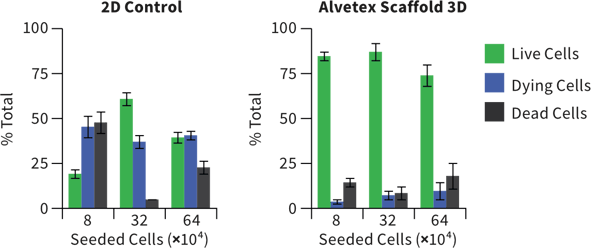
Alvetex provides an alternative method for 3D growth of keratinocytes, enabling reproduction of natural in vivo structures including the development of the stratum corneum, an essential component of the epidermal barrier. Skin constructs generated on Alvetex can then be used for drug and allergen penetration studies as well as assessment of barrier function.
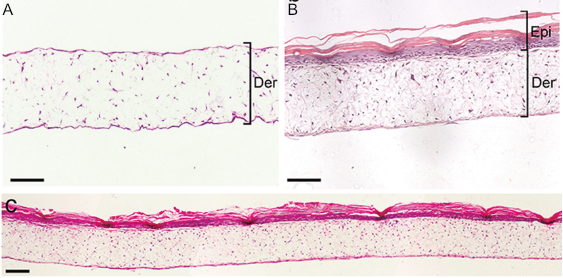
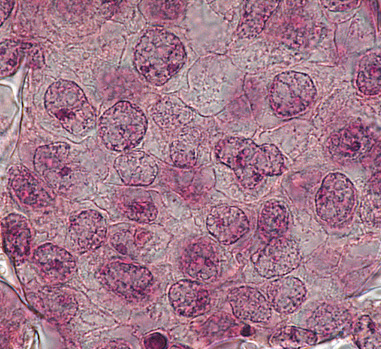
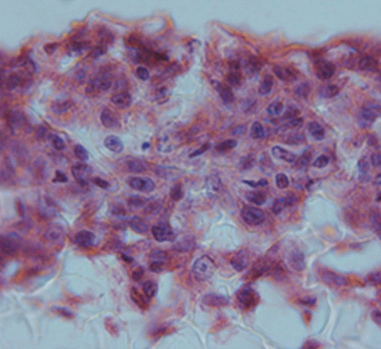
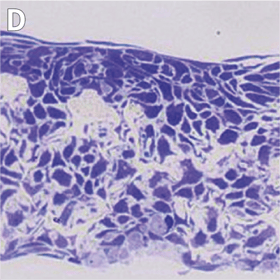
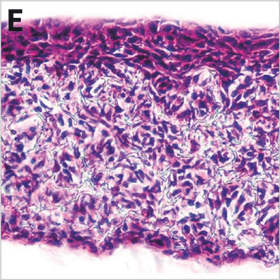
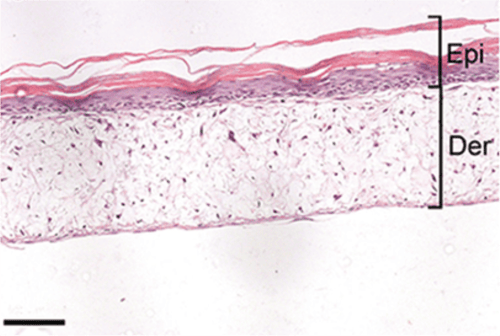
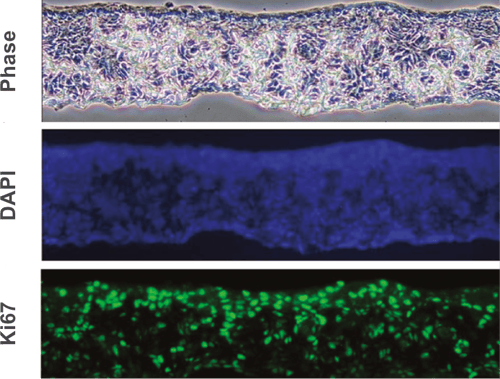
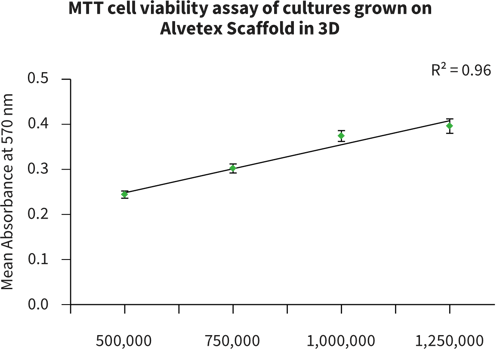
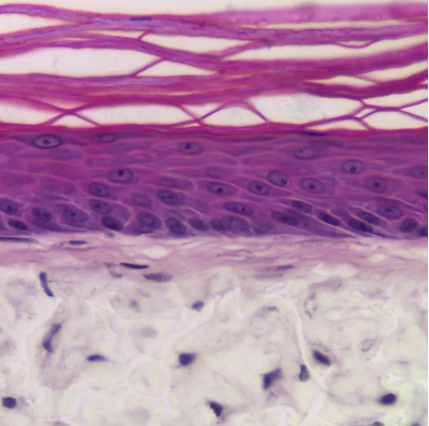
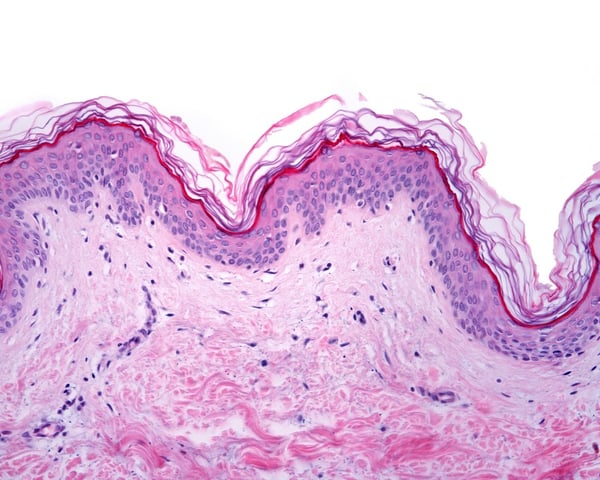
Above: Histology images showing a full thickness skin construct grown by co-culturing human dermal fibroblasts inside Alvetex Scaffold and human keratinocytes on top, thus replicating both the dermal and epidermal compartments. Note that the presence of a stratum corneum is also evident. Validation of dermal and epidermal structure in full-thickness human skin equivalents. A: Representative photomicrographs of haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained Alvetex Scaffold seeded with human dermal fibroblasts after culture in Media A for 18 days. B & C: Representative photomicrographs showing H&E stained 35 day full-thickness human skin equivalents at 20× and 10× magnification respectively.*
* Data generated during a collaborative project between Reinnervate Ltd and Newcastle University – data now published in the following paper: A Novel Fully Humanized 3D Skin Equivalent to Model Early Melanoma Invasion. Authors: D.S. Hill, N.D. Robinson, M. P. Caley, M. Chen, E.A. OʼToole, J.L. Armstrong, S. Przyborsky and P.E. Lovat. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 November ; 14(11): 2665–2673. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0394.
Resources on Alvetex and imaging techniques
Protocols:
- Cell visualization
- Advanced microscopy:
See also Histology protocols in Sectioning and Counterstaining below.
Whitepapers:
Coating
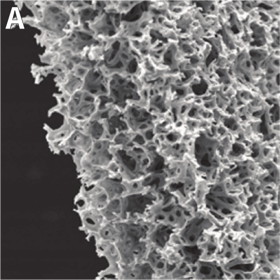
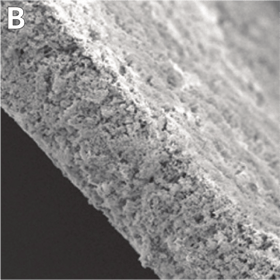
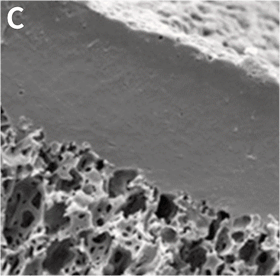
Alvetex can be coated with extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins and other reagents commonly used to treat cell culture substrates, notably: Collagen I; Collagen IV; Fibronectin; Laminin; Poly-D-lysine; Poly-L-lysine; Poly-D-lysine and Laminin; Poly-L-orthinine and Laminin; Matrigel™; PuraMatrix™.
A
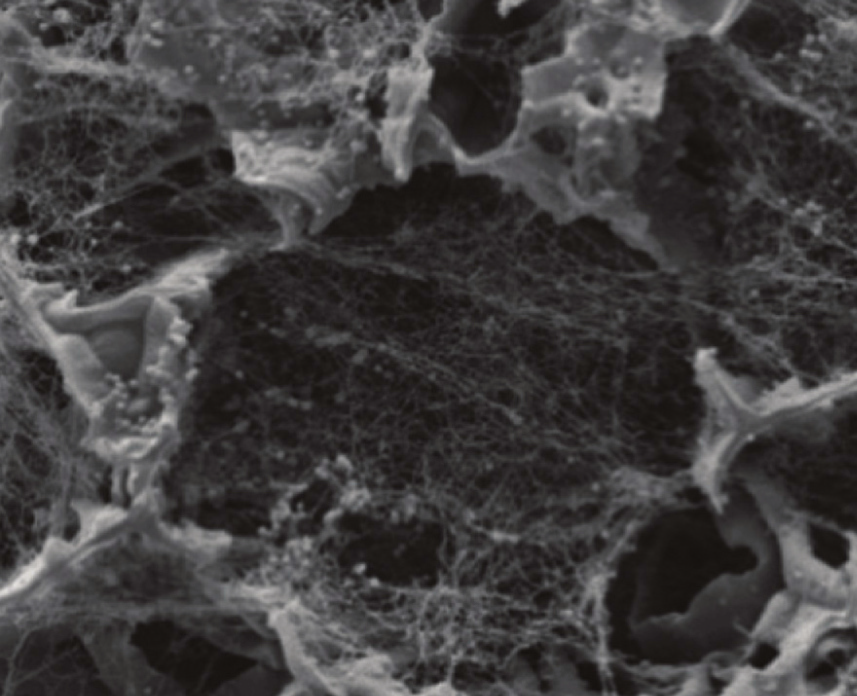
B
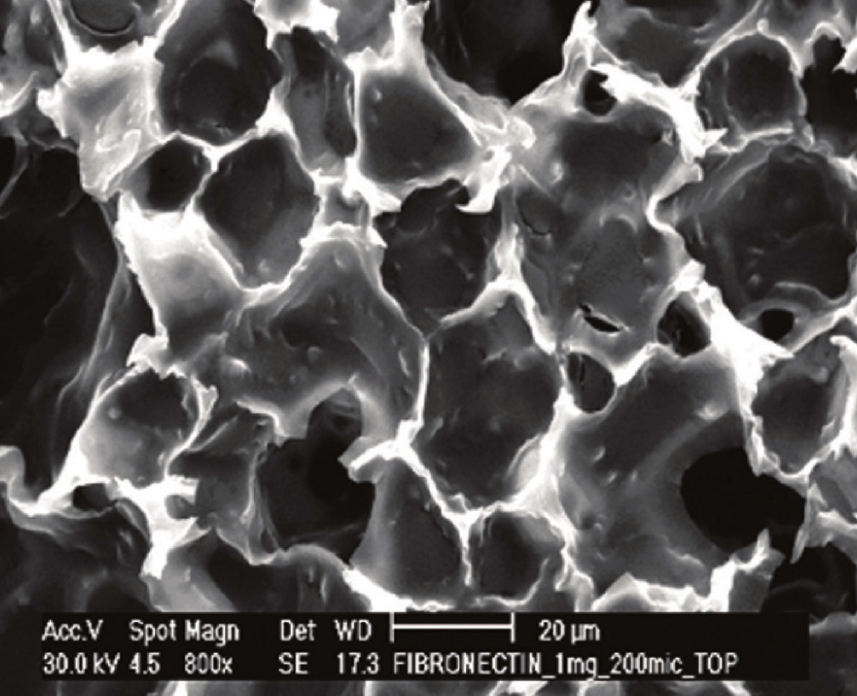
C
A: Scaffold pre-loaded with Collagen IV. B: Coating Alvetex Scaffold with fibronectin. C: Coating Alvetex Strata with Collagen I (2 mg/mL shown). The ECM proteins form a web of fibers spanning voids into which cells can grow and migrate in 3D. Depending on the ECM concentration used, this coating can either encourage cell invasion into the scaffold or create a barrier between two co-cultured cell populations.
Resources on coating Alvetex for cell culture
Protocols:
Explanting
Directly explanted cells can move into Alvetex directly from pieces of primary tissue or cell aggregates, migrating freely into the scaffold and spreading throughout its structure. Depending on cell type and characteristics, cells may proliferate as well as migrate. By enabling cells to be explanted in this way, Alvetex creates the opportunity for many different applications including tumor cell biology, separation of alternative cell types and establishing and maintaining 3D cultures de novo directly from primary sources, etc.
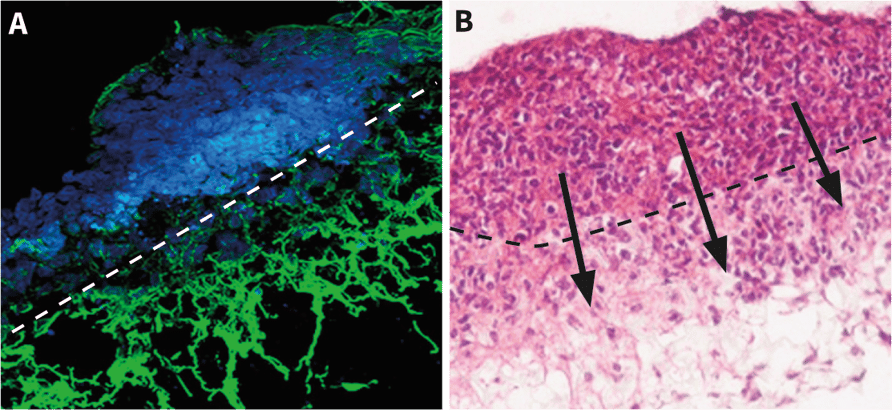
Above: Examples of cells from tissue pieces placed on top of Alvetex Scaffold migrating into the structure of the scaffold. A: A neural aggregate generated on a low-adherence plate before transfer to Alvetex Scaffold shows extensive neurite elongation within the thickness of the scaffold. B: Cells from an embryonal carcinoma aggregate readily invade Alvetex Scaffold.
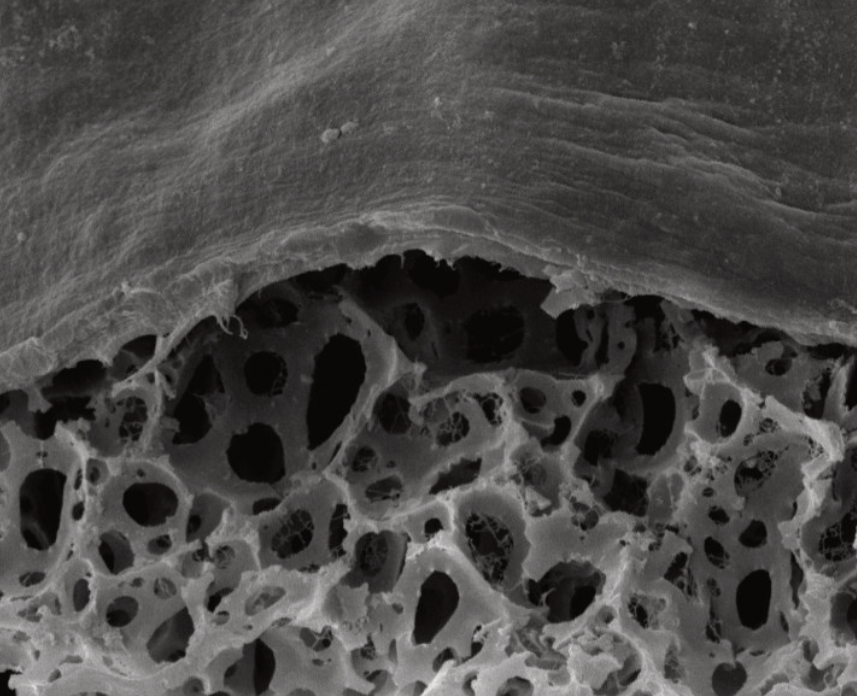
Freshly-obtained intact tissues can also be maintained directly on Alvetex Strata for improved adherence and stability during imaging.
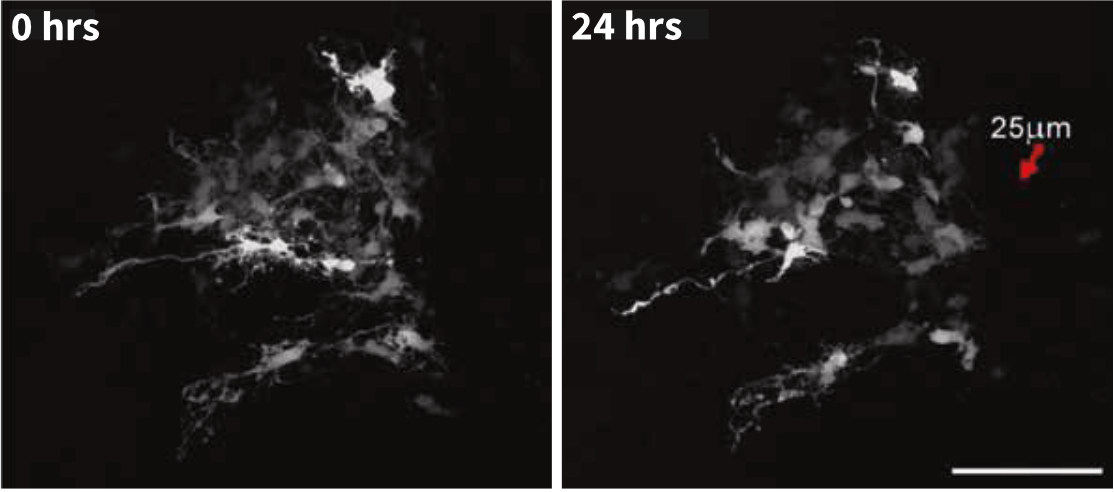
Above: Time lapse imaging of spinal cord tissue slice maintained on Alvetex Strata demonstrates minimal tissue drift over a period of 24 hours.
(Images courtesy of Kieran McDermott, University of Cork.)
Transfection
Various types of cells can be transfected using Alvetex 3D cell culture.
In collaboration with Mirus Bio, methods have been developed that enable the transfection of cells grown in Alvetex 3D culture. Common cell types (CHO-K1, HeLa, HepG2, MCF-7 and NIH-3T3) were seeded at optimized cell densities in 12 well Alvetex Scaffold 3D plates and adapted to 3D culture conditions for 48 hours. After adaptation, cells were transfected with a novel Mirus Bio formulation combined with a plasmid encoding firefly luciferase at the reagent-to-DNA ratios indicated beneath the bars. Luciferase activity was measured 24 hours post-transfection using a conventional assay. High expression was detected in all cell types demonstrating the efficiency of the Mirus Bio TransIT® 3D Transfection Reagent (MIR 5804) when used with Alvetex Scaffold 3D culture plates.
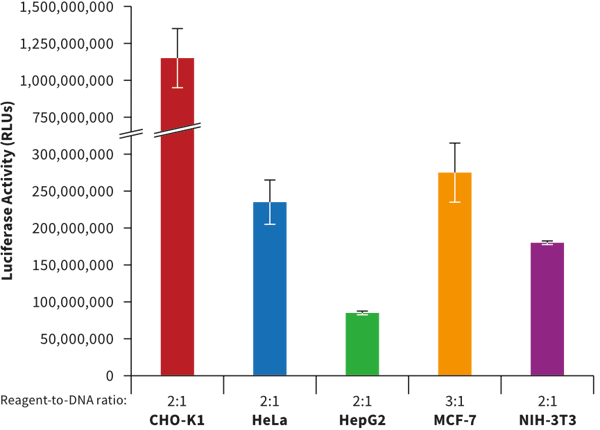
3D transfection of multiple cell types.
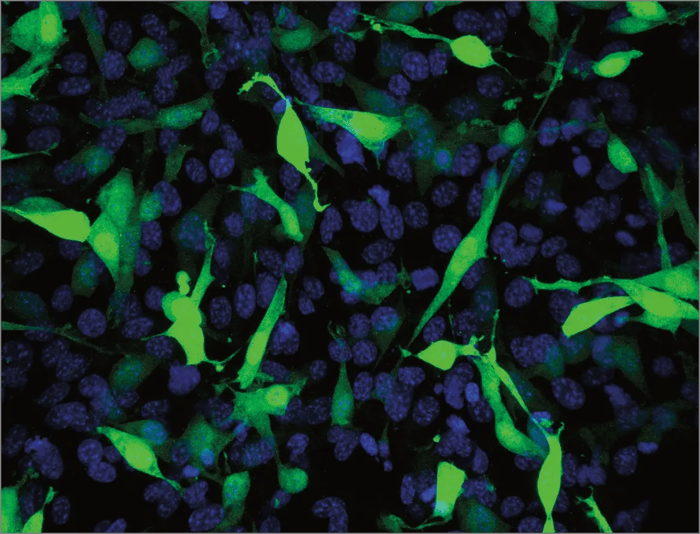
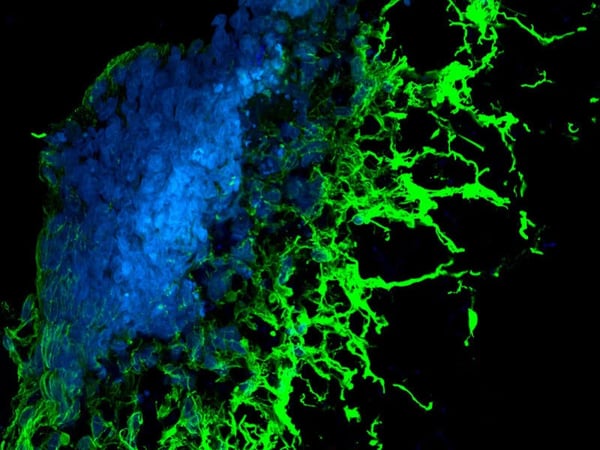
Above: Fibroblasts grown in 3D using Alvetex Scaffold were successfully transfected with a GFP construct and imaged using confocal microscopy. In brief, cells were transfected with the new Mirus Bio Transfection Reagent for 3D transfection at a reagent-to-DNA ratio of 3:1 using a GFP-expressing plasmid. Cells were seeded at 48 hours prior to transfection, and the cultures were fixed 24 hours post-transfection. Cells were imaged using a confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM510). The data shows a 40 μm integrated stack of multiple images as viewed from above the intact 3D culture. The position of all the cell nuclei are visualized with Hoechst 33342 (blue) and the positively transfected cells express GFP (green).
Co-culture
Advancing from single cell mono-cultures and co-cultures in conventional 2D models, Alvetex Scaffold provides the next step towards replicating the in vivo environment by providing the architecture necessary for 3D cell culture in vitro. Alvetex’s extremely high porosity allows cells to penetrate, grow and proliferate throughout the material for highly effective and reproducible 3D cell culture. Cells are freely able to form complex interactions with adjacent cells and receive and transmit signals, enabling a more natural environment to foster the native architecture found in tissues.
As well as being able to study single cultures in 3D, Alvetex Scaffold provides a support that enables the co-culture of more than one cell type. The structure of tissues is often comprised of discrete layers of distinct cell types. Growing different cell types in 3D, inside and on the surface of Alvetex Scaffold, enables users to re-create such tissue structures in vitro. A variety of cell co-culture scenarios can be set up to study different cell-cell interactions, according to the requirements of the cells and the dynamics under investigation.
Key benefits and applications:
- Study interactions between distinct cell types in 3D culture
- Recreate in vivo tissue morphology
- Recreate specific niche environments for disease modelling or drug testing
- Customize co-culture setup to suit the cell types involved
Several alternative approaches for co-culture design can be utilised. Alvetex Scaffold is a versatile technology that enables users to create co-culture models in many different ways.
Assembly of Co-culturing Experiments
Key to image parts:
Alvetex Scaffold
in standard multiwell plate
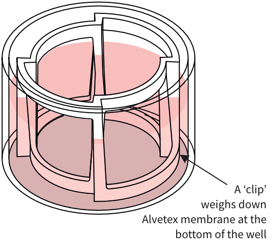

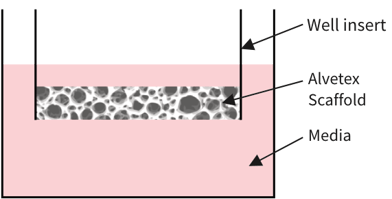
Simplified diagram:
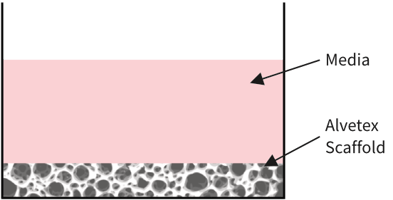
Alvetex Scaffold in well insert
in standard multiwell plate

Simplified diagram:

Alvetex Scaffold
Cell type A growing in 3D within Alvetex Scaffold
Cell type B growing in 3D within Alvetex Scaffold
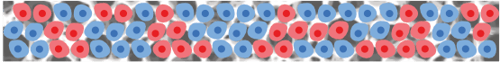
Mix of cells A & B in 3D within Alvetex Scaffold

Cells growing in 2D (monolayer)
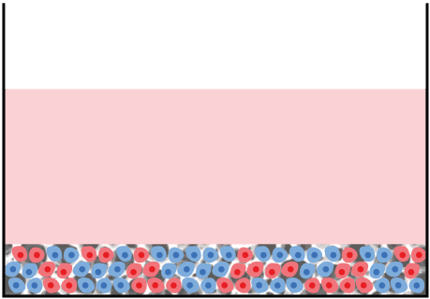
Assembly option 1 – 3D co-culture in multiwell plate or well insert:
Description: Different cell types cultured together within the same scaffold.
Application: Emulate the structure of a tissue comprised of more than one cell type.
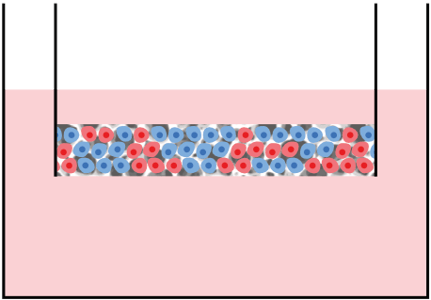
Assembly option 2 ‐ 3D / 2D co-culture in multiwell plate and well insert combined:
Description: Different cell types cultured together within the same scaffold within a well insert.
Application: Approach used to study the secretion of factors and signaling molecules.
Assembly option 3 ‐ 3D co-culture in multiwell plate and well insert combined:
Description: Two independent 3D cultures. Contact is via medium – communication via paracrine factors.
Application: Approach used to study the secretion of factors and signaling molecules.
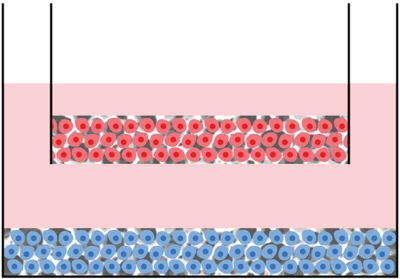
Assembly option 4 ‐ 3D / 3D co-culture in multiwell plate:
Description: Two 3D cultures in direct contact with one another.
Application:
- Study the direct interaction of cells in contact with one another.
- To establish layers of alternate cell types in 3D to mimic tissue structures.
- To investigate invasion and migration of different cell types amongst each other.
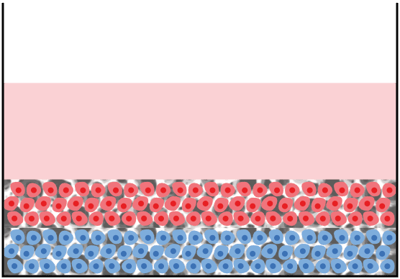
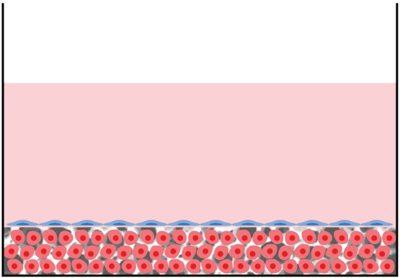
Assembly option 5 ‐ 2D / 3D co-culture in multiwell plate:
Description: One 2D (monolayer) and one 3D culture layered in direct contact with one another
Application:
- Study the direct interaction of cells in contact with one another
- To establish layers of alternate cell types in 3D to mimic tissue structures
- To investigate invasion and migration of different cell types amongst each other
Exmples of Co-culturing Experiments
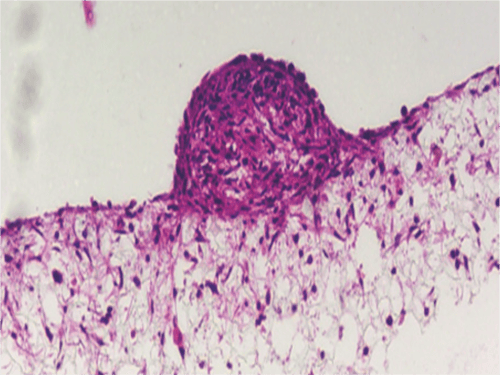
Above: Co-culture of glial and neural cells to model brain tissues. Brightfield micrograph showing the structure of a human stem cell-derived neurosphere co-cultured for 7 days with U118-MG glial cells on Alvetex Scaffold presented in the 12-well insert in 12-well plate format.
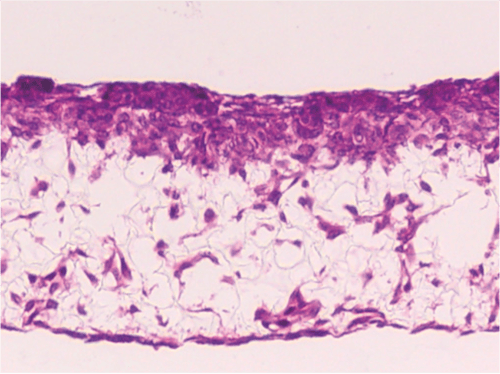
Above: Cell invasion into Alvetex Scaffold. Brightfield micrograph showing the structure of SW480 colon adenocarcinoma cells co-cultured for 7 days with established 3D cultures of 3T3 fibroblasts on Alvetex Scaffold.
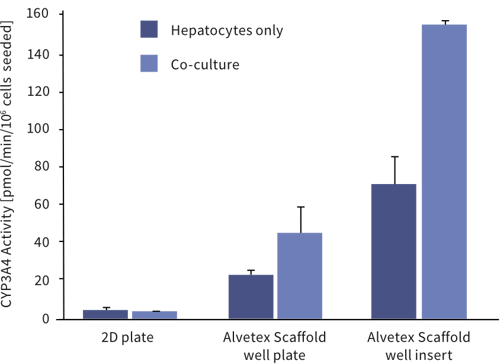
Above: Enhanced cell function with hepatocyte and endothelial cell co-culture. The activity of CYP3A4 in upcyte® hepatocytes cultured on a 2D plate and on Alvetex Scaffold presented in both a 12-well plate and 6-well insert formats. Hepatocytes were grown as mono-cultures and also co-cultured with upcyte® micro-vascular endothelial cells for 10 days. For further details please visit www.medicyte.com.
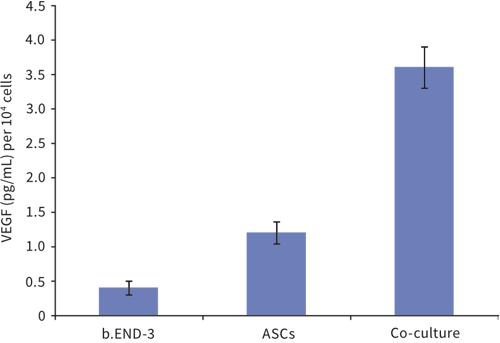
Above: Co-culture of adipose tissue-derived stem cells with endothelial cells influences their differentiation. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ASCs) and endothelial cells (b.END-3) were cultured independently and as co-cultures in Alvetex Scaffold 12 well plate format for 3 days. Data from 3 sample replicates. VEGF levels normalized to the number of cells at the time of seeding, expressed as pg/mL per 10 cells. For further details please refer to Neofytou, E.A., et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells display a proangiogenic phenotype on 3D scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011; 98(3): 383-93.
Resources on co-culturing cells in Alvetex
Protocols:
Some scientific papers featuring Alvetex co-cultures:
- In vitro toxicity of glyphosate in Atlantic salmon evaluated with a 3D hepatocyte-kidney co-culture model
L.Søfteland and P.A.Olsvik
Food and Chemical Toxicology, Volume 164. 14 April 2022. DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113012
- Bioengineering Novel in vitro Co-culture Models That Represent the Human Intestinal Mucosa With Improved Caco-2 Structure and Barrier Function
Nicole J Darling, Claire L Mobbs, Ariana L González-Hau, Matthew Freer and Stefan Przyborski
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 31 August 2020. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00992
- Characterization of liver specific functions of upcyte® hepatocytes grown in 3D and co-cultured with upcyte® endothelial cells
Dähn C, Hewitt N, Maltman D, Talas G, Przyborski S, Heinz S, Nörenberg A, Scheller K, Braspenning J
Z Gastroenterol, 2012; 50 - P2_05. 2012. DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1295802