Culture of the Canine Kidney Epithelial MDCK Cell Line on Alvetex® Scaffold in Well Insert and Well Plate Formats
● Download this protocol as a PDF (3.9 MB)
1. Introduction
MDCK is a canine kidney cell line isolated in the late 1950s from normal cocker spaniel tissue[1]. With time, several strains of MDCK were developed, which differ in terms of cell size, tubulogenesis potential and polarity markers expression [2]. MDCK cells have been extensively used to study protein trafficking and the establishment of cell polarity in epithelia[3,4], but also have more applied uses such as viral production for the vaccine industry[5].
Alvetex Scaffold is available in several cell culture formats including 24 well plate (AVP006), 12 well plate (AVP002), 6 well insert (AVP004), 12 well insert (AVP005), and 24 well insert (AVP012).
24 well and 12 well plates are suitable for shorter term cultures and for applications where limited cell penetration into the scaffold is required. Well insert formats generally support longer term cultures and deeper cell penetration into the scaffold. They also provide for conveniently tailored media set ups (see the Alvetex Scaffold Quick Start protocol).
The availability of two different well insert formats enables choice on the basis of desired culture size and cell expenditure. 6 well inserts can be placed in conventional 6 well plates, while 12 well inserts can be placed in either 6 well plates or 12 well plates, depending on media requirements. Alternatively, both insert types can be housed in the dedicated Well Insert Holder in Deep Well Petri Dish (AVP015) to allow for increased media volumes and prolonged cell culture.
Here, we present protocols for the culture of MDCK cells on both 6 well insert and 24 plate formats. For more information about the culture of epithelial monolayers on Alvetex Scaffold, with or without a collagen layer, please refer to the Application Note dedicated to the Growth of Simple Epithelia.
2. Methods
2.1. Preparation for 3D Cell Culture on Alvetex Scaffold
- MDCK cells (ECACC, 84121903) were routinely maintained in T-75 flasks.
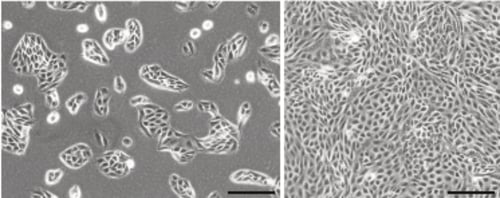
Figure 1. Phase contrast micrograph of MDCK cells grown in conventional 2D culture plates. Image shows cells at low (left) and high (right) confluency. Scale bars: 200 µm.
-
Complete growth media consisted of: Minimum Essential Medium (MEM) supplemented with 10 % v/v FBS, 0.1 mM non-essential amino acids, 2 μM L-glutamine and 100 U/mL Penicillin/Streptomycin.
-
Cells were harvested by trypsinisation and centrifuged for 5 minutes (1000 rpm). The supernatant was discarded and the cell pellet was re-suspended in an appropriate volume of media for cell counting by Trypan Blue.
-
Cells were re-suspended at a concentration of 1.0 × 106 cells/mL for seeding.
2.2. 6 Well Insert Format (AVP004)
-
Alvetex Scaffold 6-well inserts in 6-well plate format were prepared for seeding by dipping in 70 % ethanol followed by media washes (twice with 10 mL per well).
-
Wells were filled from the outside of the insert with enough medium to allow it to rise inside the insert and cover the substrate, but not to go over the sides of the inserts, i.e. 7 mL ± 1 mL, as described for feeding above and below separately in the Alvetex Scaffold Quick Start Protocol.
-
250 μl of the cell suspension was added in droplets over the surface of the Alvetex Scaffold disc, which was equivalent to 0.25 × 106 cells per well.
-
The plate was incubated overnight at 37 °C with 5 % CO2 to allow the cells to settle into the scaffold.
-
Media was added to each well to a total volume of 10 mL the following morning taking care not to dislodge cells from the Alvetex Scaffold.
-
Plates were re-incubated and maintained by complete media exchange every other day.
Note: This method can be applied to the use of Alvetex Scaffold in 12-well insert format, AVP005. Adjust cell seeding and media volumes according to the guidelines provided in the Alvetex Scaffold Quick Start Protocol.
2.3. 24 Well Plate Format (AVP006)
-
Alvetex Scaffold 24-well plates were prepared for seeding with a 70 % ethanol wash (2 mL per well) and subsequent media washes (twice with 2 mL of media each).
-
125 μL of the cell suspension was added in droplets over the surface of the Alvetex Scaffold disc, which was equivalent to 0.125 × 106 cells per well.
Note: This method can be applied to the use of Alvetex Scaffold in 12-well plate format, AVP002. Adjust cell seeding and media volumes according to the guidelines provided in the Alvetex Scaffold Quick Start Protocol.
-
The plate was incubated for at least 1 hour at 37 °C with 5 % CO2 to allow the cells to settle into the scaffold.
-
2 mL of media was added to each well taking care not to dislodge cells from the Alvetex Scaffold.
-
Plates were re-incubated and maintained by complete media exchange every other day.
3. Example Data
3.1. 6 Well Insert Format (AVP004)
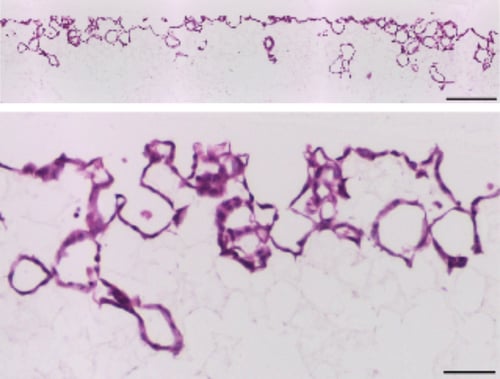
Figure 2. Brightfield micrographs showing the structure of MDCK cells cultured for 7 days on 22mm diameter Alvetex Scaffold discs presented in 6 well insert format. Cells were fixed, embedded in paraffin wax, sectioned (10 µm) and counterstained with haematoxylin and eosin. Scale bars: 200 µm (top) and 50 µm (bottom).
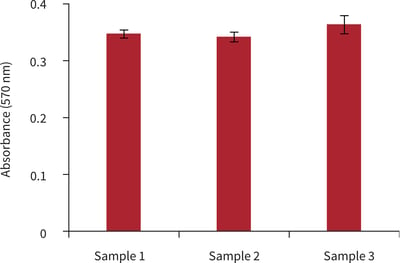
Figure 3. Biochemical analysis of cell viability using a standard MTT assay. Data from 3 sample replicates of MDCK cells are shown, each sampled in triplicates (n = 3, mean ± SD). Cells were cultured for 3 days on 22 mm Alvetex Scaffold discs presented in 6-well inserts in 6 well plate format.
3.2. 24 Well Plate Format (AVP006)
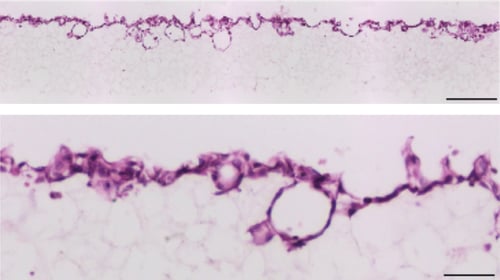
Figure 4. Brightfield micrographs showing the structure of MDCK cells cultured for 7 days on 15 mm diameter Alvetex Scaffold discs presented in 24 well plate format. Cells were fixed, embedded in paraffin wax, sectioned (10 μm) and counterstained with haematoxylin and eosin. Scale bars: 200 µm (top) and 50 μm (bottom).
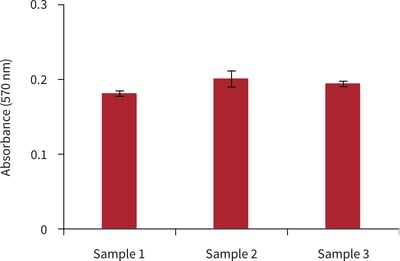
Figure 5. Biochemical analysis of cell viability using a standard MTT assay. Data from 3 sample replicates of MDCK cells are shown, each sampled in triplicates (n = 3, mean ± SD). Cells were cultured for 3 days on 15 mm Alvetex Scaffold discs presented in 24 well plate format.
4. References
-
Gaush CR et al, 1966. Characterization of an established line of canine kidney cells (MDCK). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 122(3):931-5.
-
Dukes JD et al, 2011. The MDCK variety pack: choosing the right strain. BMC Cell Biol 12:43-6.
-
Odorizzi G et al, 1996. Apical and basolateral endosomes of MDCK cells are interconnected and contain a polarized sorting mechanism. J Cell Biol 135(1):139-52.
-
Wang AZ et al, 1990. Steps in the morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium. I. Uncoupling the roles of cell-cell and cell-substratum contact in establishing plasma membrane polarity in multicellular epithelial (MDCK) cysts. J Cell Sci 95(1):137-51.
-
Chu C et al, 2009. Conversion of MDCK cell line to suspension culture by transfecting with human siat7e gene and its application for influenza virus production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(35):14802-7.