Transport Studies in 3D Bioengineered IBD Model
Drug Discovery Assay – reference number: B126
Overview
| Tissue: | Bioengineered human IBD tissue |
| Target: | n/a |
| Control compound: | BIRB796, 5-ASA, prednisolone, tofacitinib |
| Study type: | 3D cell culture |
| Functional endpoint: | Ion channel function, permeability, metabolism |
Drug treatments reverse LPS-mediated increases in permeability
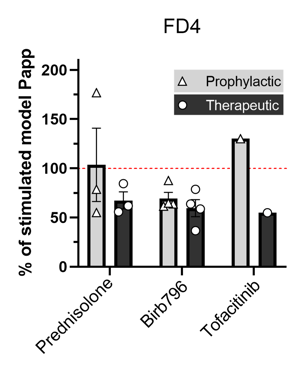 Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-dextran (FD4) is a marker of permeability. Treatment with 10 µM BIRB796, Prednisolone, and Tofacitinib reverses LPS-mediated increases in permeability (Papp). n=1-4 independent experiments.
Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-dextran (FD4) is a marker of permeability. Treatment with 10 µM BIRB796, Prednisolone, and Tofacitinib reverses LPS-mediated increases in permeability (Papp). n=1-4 independent experiments.
Testing Information
Assay Description
This assay assesses the permeability of test articles in a 3D Bioengineered model for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The specific results that will be provided are the effects of test articles on transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER), or permeability.
Test Article Requirements
Test article(s) to be provided by the Sponsor in storable aliquots at required test concentrations with information on the diluent vehicle used. Stock solutions are prepared in distilled water unless otherwise requested. Sponsor to provide sufficient test article to run the entire study.
Suggested Testing
A minimum of triplicate per condition with a maximum of 48 models per experiment. Several experiments can be run in a single study to increase model throughput.
Study Outline
Rationale and Experimental Design
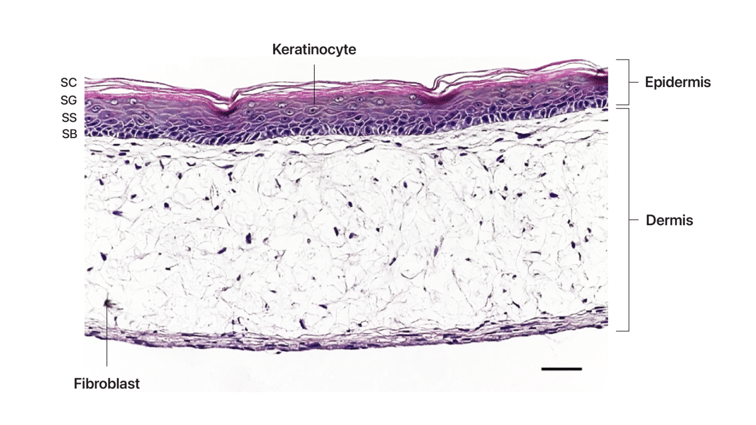
To form tissue layers that mimic inflamed IBD mucosa, our researchers culture three different cell types in Alvetex® Scaffold inserts. Fibroblasts are seeded first to generate abundant endogenous ECM and growth factors to support other cell types. Differentiated immune cells are then added to create a viable immune component and form a relevant lamina propria compartment. As these immune cells contain an NFκB reporter, their activation can be easily quantified using a colorimetric assay. Finally, epithelial cells are added to create a confluent microvilli brush-border, mimicking the lining of the human intestine. Once the cells have matured, the model is stimulated (usually with LPS) and can be cultured for up to 21 days.
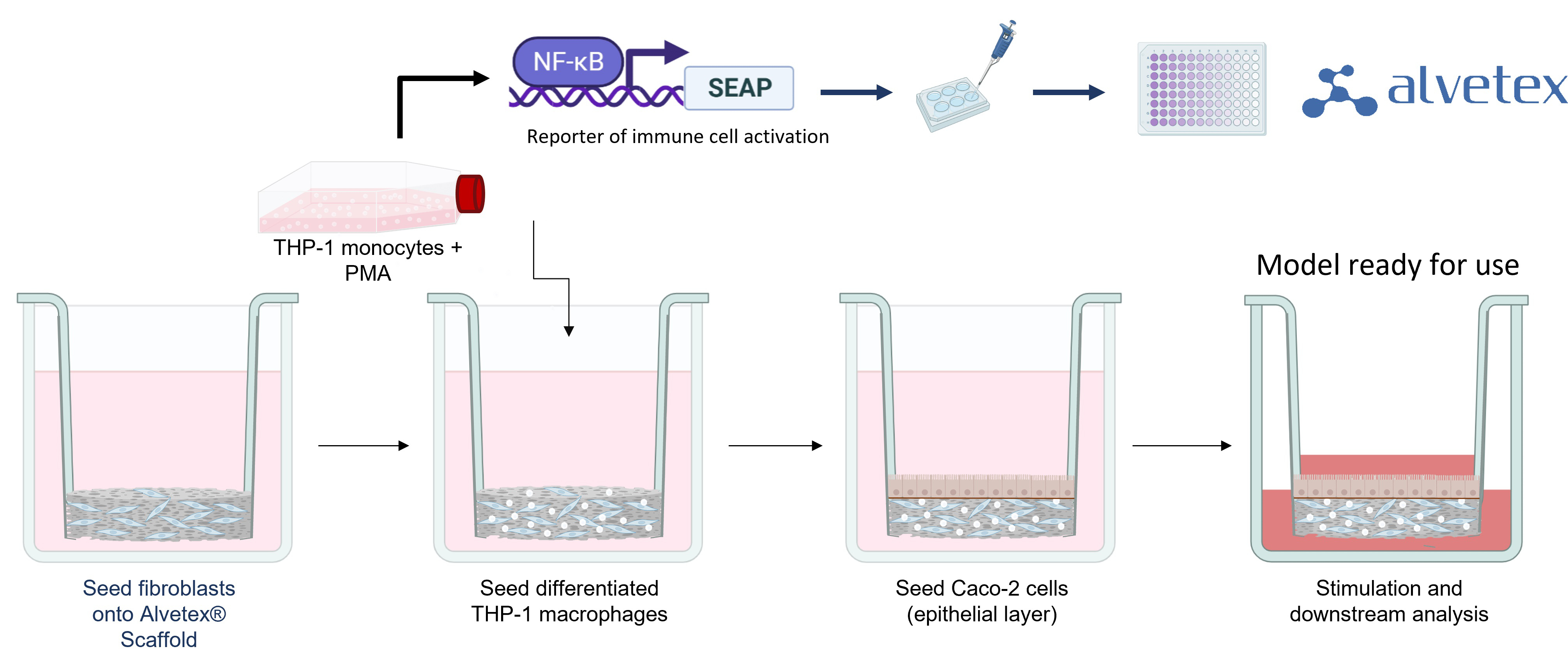
Addition of Test Articles
Test articles can be added directly to the culture medium (no carrier required). It is recommended a minimum of triplicates should be used for each condition. An example of the conditions assessed for three test agents would be as follows:
- Non-stimulated control
- Stimulated control
- Test agent 1
- Test agent 2
- Test agent 3
- Positive control
End Point Analysis
There is a range of endpoints that can be used with this model including transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER), or permeability (Papp).
Example data
Pharmacological blockage of inflammatory response reduces barrier permeability
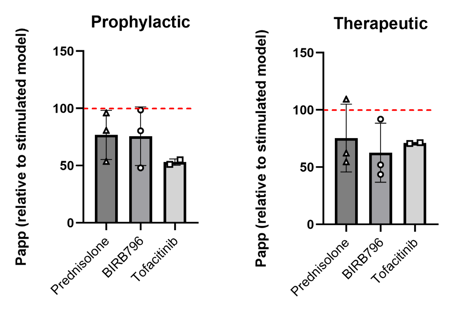 Pharmacological blockage of inflammatory response reduces barrier permeability. FD4 transport assay used to assess paracellular permeability. Prednisolone, BIRB796, and Tofacitinib (10 μM) prevent or rescue barrier permeability induced by LPS stimulation. Data expressed relative to permeability (Papp) of stimulated models. Reduction in Papp suggests decreased permeability compared to stimulated controls.
Pharmacological blockage of inflammatory response reduces barrier permeability. FD4 transport assay used to assess paracellular permeability. Prednisolone, BIRB796, and Tofacitinib (10 μM) prevent or rescue barrier permeability induced by LPS stimulation. Data expressed relative to permeability (Papp) of stimulated models. Reduction in Papp suggests decreased permeability compared to stimulated controls.
Protective vs. restorative effect of pharmacological compounds on immune activation
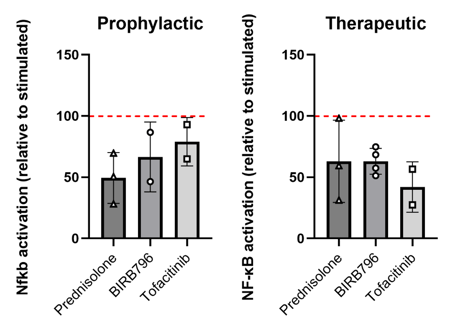
Pharmacological blockage of inflammatory response reduces NF-κB activation. Prednisolone, BIRB796 and Tofacitinib (10 μM) suppress NF-κB activation in immune cells in stimulated models. Values are relative to stimulated controls. Data presented as mean of 3 IBD models per experimental repeat ± SEM. Examined the effect of each drug compound on NFkB activation within the models – done using a promotor-based colorimetric assay. Both therapeutic and prophylactic treatments reduced immune cell activation within models.