Recombinant human follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein
QK035
Brand: Qkine
Follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein has been engineered to prevent binding to the natural inhibitor, follistatin. In vivo activin A activity is regulated by follistatin, a high-affinity inhibitor; follistatin accumulates in stem cell culture, where it inhibits activin A.
Qk035 follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) has equivalent bioactivity to wild-type activin A (Qk001) but does not bind follistatin so is resistant to feedback inhibition. High purity 26 kDa dimer comprising engineered mature domain of activin A protein, animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier-protein free (CF). This specialized activin A has been developed in Marko Hyvönen’s group in the University of Cambridge.
Currency:
| Product name | Catalog number | Pack size | Price | Price (USD) | Price (GBP) | Price (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant human/mouse/rat follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein, 25 µg | QK035-0025 | 25 µg | (select above) | $ 340.00 | £ 250.00 | € 292.00 |
| Recombinant human/mouse/rat follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein, 50 µg | QK035-0050 | 50 µg | (select above) | $ 520.00 | £ 380.00 | € 444.00 |
| Recombinant human/mouse/rat follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein, 100 µg | QK035-0100 | 100 µg | (select above) | $ 685.00 | £ 500.00 | € 584.00 |
| Recombinant human/mouse/rat follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein, 500 µg | QK035-0500 | 500 µg | (select above) | $ 27775.00 | £ 2025.00 | € 2366.00 |
| Recombinant human/mouse/rat follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein, 1000 µg | QK035-1000 | 1000 µg | (select above) | $ 4370.00 | £ 3190.00 | € 3726.00 |
Note: prices shown do not include shipping and handling charges.
Qkine company name and logo are the property of Qkine Ltd. UK.
Alternative protein names
Species reactivity
human
species similarity:
mouse – 98%
rat – 98%
porcine – 98%
bovine – 98%
Summary
- High purity mature domain of follistatin-resistant activin A protein
- >98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
- 26 kDa (dimer)
- Expressed in E. coli
- Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free.
- Manufactured in Qkine's Cambridge, UK laboratories
- Lyophilized from acetonitrile, TFA
- Resuspend in 10 mM HCl at >100 µg/ml (provided with protein and free of charge), prepare single use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired and store frozen at -20°C or -80°C
Featured applications
- Induced pluripotent and embryonic stem cell differentiation and maintenance
Bioactivity
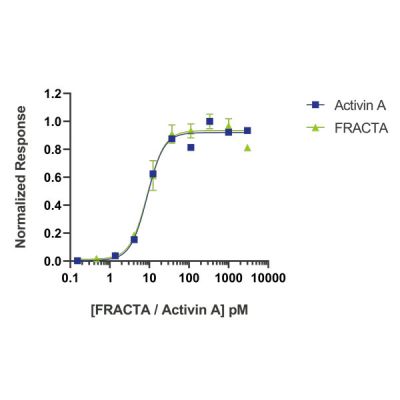
Activin A protein activity is determined using an activin-responsive firefly luciferase reporter in HEK293T cells. EC50 for wild-type activin A (Qk001) = 0.228 ng/ml (8.776 pM), EC50 for follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA, Qk035) = 0.228 ng/ml (8.792 pM).
Purity
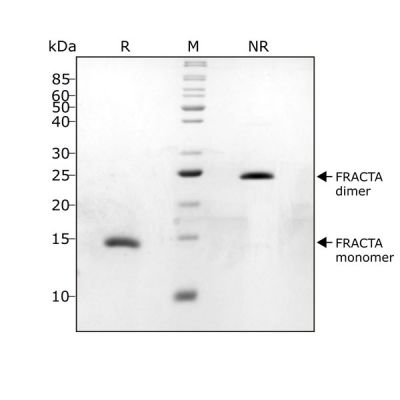
FRACTA migrates as a single band at 24 kDa in non-reducing (NR) and 13 kDa as a single monomeric species upon reduction (R). No contaminating protein bands are visible. Purified recombinant protein (1 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptothanol, R) and non-reduced conditions (NR) and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk035 lot #104287.
Further quality assays
- Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
- Analytical reversed-phase: single sharp peak
- Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
- Recovery from stock vial: >95%
Protein background
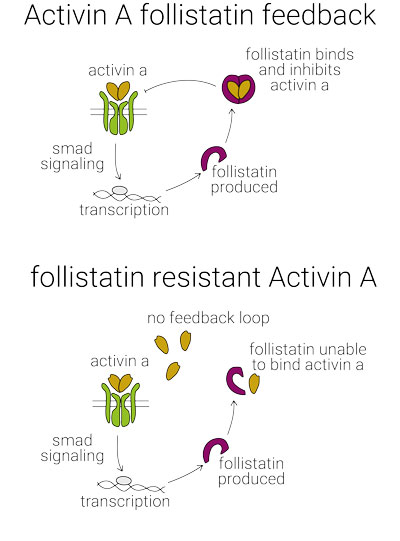
Human activin A protein is a member of the TGF-β superfamily of growth factors involved in stem cell differentiation and maintenance, regulation of embryogenesis, development of the reproductive system, wound healing and regulation of immune responses. Activin A signaling is modulated by the glycoprotein follistatin, production is which is stimulated by activin A forming a feedback loop [1], and inhibins.
Follistatin binds to and neutralises members of the TGF-β superfamily, preventing signalling by shielding the type II and I receptor binding sites [2-4].
Activins are disulfide-linked homo- and heterodimers of four inhibin β chains. The best characterized are activin A and activin B, homodimers of inhibin βA and inhibin βB respectively. Activins, like all other members in the TGF-β superfamily, are synthesized as larger precursors consisting of an N-terminal signal peptide, a pro-domain of 250–350 residues and a highly conserved mature domain. The pro-domain, which is cleaved off in the mature protein, has important roles in the biosynthesis, stabilization, transportation and signalling of the growth factors [5].
Recombinant activin A is used for maintenance of pluripotency in many human induced-pluripotent stem cell and human embryonic stem cell lines [3], and to induce stem cell differentiation into endoderm [6] and other cell fates.
Follistatin resistant activin A (FRACTA) has been developed in the lab of Marko Hyvönen at the University of Cambridge. FRACTA has been engineered to be unimpeded by follistatin while maintaining its ability to bind type I and II receptors.
Background references
- Harrington, A. E. et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of activin signalling by follistatin. EMBO J. 25, 1035–1045 (2006). doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601000
- Wang, X., Fischer, G. & Hyvönen, M. Structure and activation of pro-activin A. (2016). doi:10.1038/ncomms12052
- Jones, K. L., Kretser, D. M. de, Patella, Shane. & Phillips, D. J. Activin A and follistatin in systemic inflammation. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 225, 119–125 (2004). doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2004.07.010
- Walton, K. L., Makanji, Y. & Harrison, C. A. New insights into the mechanisms of activin action and inhibition. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 359, 2–12 (2012). doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.06.030
- Pauklin, S. & Vallier, L. Activin/Nodal signalling in stem cells. Development 142, 607–19 (2015). doi.org/10.1242/dev.091769
- D’Amour, K. A. et al. Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 1534–1541 (2005). doi.org/10.1038/nbt1163