Stemolecule™ Sodium Butyrate
04-0005
Brand: Stemolecule™
Sodium butyrate (butyric acid sodium salt) has been shown to direct the differentiation of mouse ESCs cells into hepatocytes.
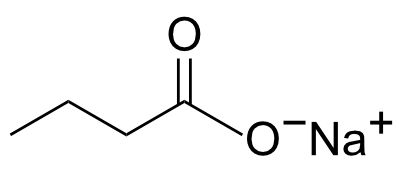
Butyric acid sodium salt
Currency:
| Product name | Catalog number | Pack size | Price | Price (USD) | Price (GBP) | Price (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stemolecule™ Sodium Butyrate | 04-0005 | 500 mg | (select above) | $ 70.00 | £ 58.00 | € 68.00 |
Note: prices shown do not include shipping and handling charges.
Product Information
Sodium butyrate is the sodium salt of the short-chain fatty acid butyric acid. It is a metabolite of intestinal bacteria, a major energy source for gut epithelial cells, and is known to play a key role in the homeostasis of the gastrointestinal tract1. Sodium butyrate is also a known inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs)2. HDAC inhibitors are promising anti-tumour agents that work by inhibiting cell proliferation and survival3. Along with the cytokines Activin A and acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF), sodium butyrate has been shown to direct the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells into hepatocytes4. Sodium butyrate has also been reported to increase the efficiency of transfection and expression for both transient and stable transfections5.

Stemgent and the Stemolecule brand name are trademarks of REPROCELL Inc., Japan.
Product Name: Stemolecule Sodium Butyrate
Catalog Number: 04-0005
Size: 500 mg
Alternate Name(s): Butyric acid sodium salt
Chemical Formula: C4H7O2·Na
Molecular Weight: 111.1
CAS Number: 156-54-7
Purity: Greater than 98 % by acid base titration
Formulation: White solid
Solubility: This molecule is soluble in water at 900 mM.
Reconstitution: For a 100 mM stock solution of Sodium Butyrate, add 9 mL of water to 100 mg of the compound. If precipitate is observed, warm the solution to 37 °C for 2 to 5 minutes. For cell culture, the medium should be prewarmed prior to adding sodium butyrate.
Storage and Stability: Store powder at 4 °C protected from light. Information about the stability of Stemolecules in solution is largely not available. For Sodium Butyrate, we recommend that stock solution be freshly made and stored in aliquots at −20 °C, protected from light. The effect of storage of stock solutions should be verified for each application.
Quality Control: The purity of Sodium Butyrate was determined by acid-base titration. The accurate mass was determined by mass spectrometry. Cellular toxicity of Sodium Butyrate was tested on HeLa and HEK293 cells.
- Säemann, M.D., Böhmig, G.A., Osterreicher, C.H., Burtscher, H., Parolini, O., Diakos, C., Stöckl, J., Hörl, W.H., Zlabinger, G.J. Anti-inflamatory effects of sodium butyrate on human monocytes: Potent inhibition of IL-12 and up-regulation of IL-10 production. FASEB J 14: 2380-2382 (2000).
- Kruh, J. Effecs of sodium butyrate, a new pharmacological agent, on cells in culture. Mol Cell Biochem 42: 65-82 (1982).
- Mühlethaler-Mottet, A., Meier, R., Flahaut, M., KBourloud, K.B., Nardou, K., Joseph, J.M., and Gross, N. Complex molecular mechanisms cooperate to mediate histone deacetylase inhibitors anti-tumor activity in neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cancer 7: 55 (2008).
- Zhou, M., Li, P., Tan, L., Qu, S., Ying, Q.L., Song, H. Differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into hepatocytes induced by a combination of cytokines and sodium butyrate. J Cell Biochem 109: 606-614 (2010).
- Goding, C.R., and Russell, W.C. S1 sensitive sites in adenovirus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 21-36 (1983).
Additional Publications
- Yuan B; Zhou X; et al.. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein forms nuclear condensates and regulates alternative splicing. Nature Commun 13:3646 (2022).
- Momcilovic O; Sivapatham R; Oron TR; Meyer M; Mooney S; Rao MA; Zeng X. Derivation, characterization, and neural differentiation of integration-free induced pluripotent stem cell lines from Parkinson's disease patients carrying SNCA, LRRK2, PARK2, and GBA mutations. PLoS ONE 11(5): e0154890. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154890 (2016).
- Zhu S; Russ HA; Wang X; Zhang M; Ma T; Xu T; Tang S; Hebrok M; Deng S. Human pancreatic β-like cells converted from fibroblasts. Nature Commun 7:10080 (2016).
- Zhu S; Wang H; Deng S. Reprogramming fibroblasts toward cardiomyocytes, neural stem cells and hepatocytes by cell activation and signaling-directed lineage conversion. Nature Protocols 10: 959-973 (2015).
- Wang J; Huang V; Ye L; Barcena A; Lin G; Lue TF; Li L-C. Identification of small activating RNAs that enhance endogenous OCT4 expression in human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Develop 24:345 (2015).
- Higuchi S; Watanabe TM; Kawauchi K; Ichimura T; Fujita H. Culturing of mouse and human cells on soft substrates promote the expression of stem cell markers. J Biosci Bioeng 117:749 (2014).