Stemolecule™ Cyclopamine
04-0022
Brand: Stemolecule™
Cyclopamine is a steroid alkaloid isolated from the corn lily (Veratrum californicum) that is a Smoothened antagonist involved in both embryogenesis and cancer progression.
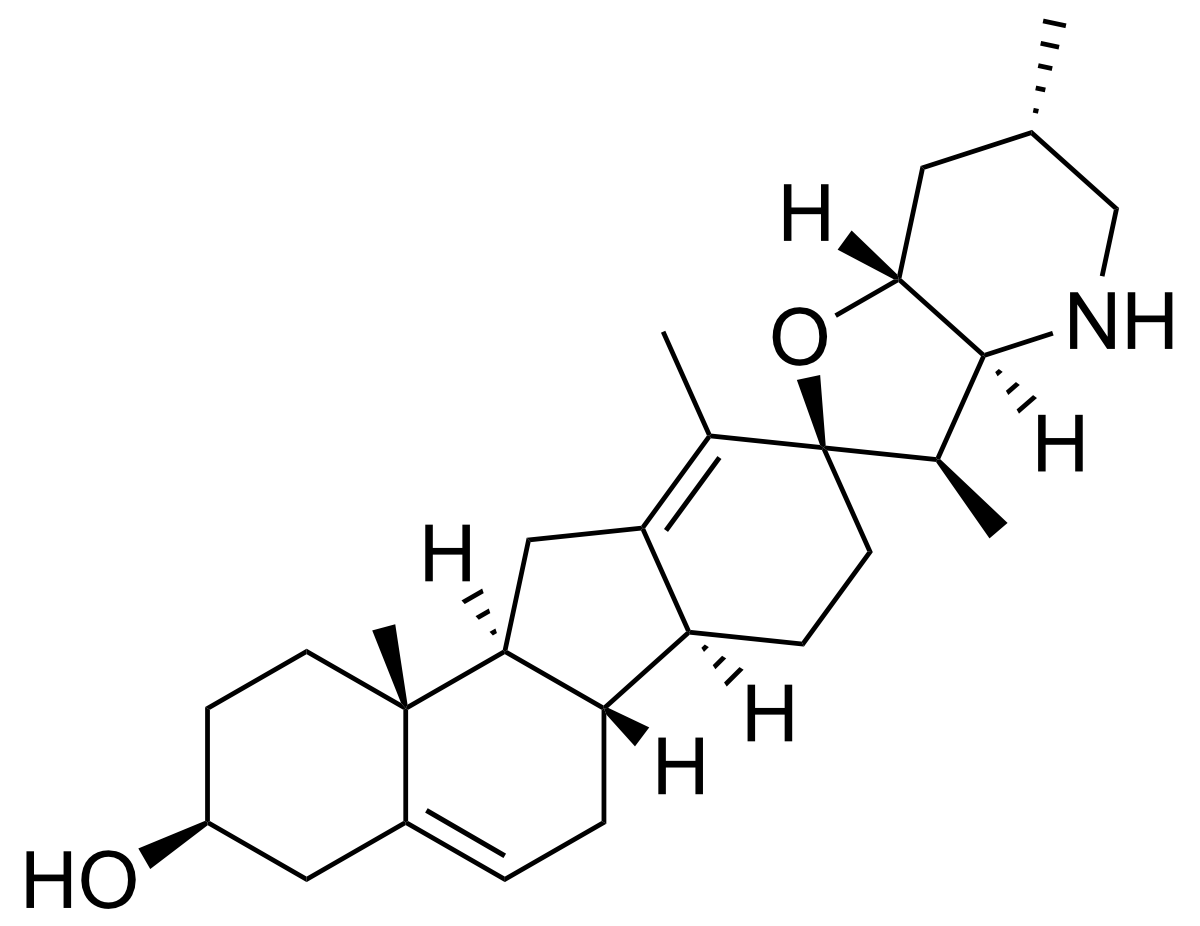
- (3S,3'R,3'aS,6'S,6aS,6bS,7'aR,9R,11aS,11bR)-3',6',10,11b tetramethylspiro[2,3,4,6,6a,6b,7,8,11,11a-decahydro-1H-benzo[a]fluorene-9,2'-3a,4,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-3H-furo[3,2-b]pyridine]-3-ol
Currency:
| Product name | Catalog number | Pack size | Price | Price (USD) | Price (GBP) | Price (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stemolecule™ Cyclopamine | 04-0022 | 2 mg | (select above) | $ 162.00 | £ 167.00 | € 195.00 |
Note: prices shown do not include shipping and handling charges.
Product Information
Stemolecule Cyclopamine is a steroid alkaloid isolated from the corn lily (Veratrum californicum) and originally identified as a teratogenic agent1. Cyclopamine has since been identified as a specific inhibitor of hedgehog signaling by direct binding to the heptahelical bundle of Smoothened2. Hedgehog signaling is involved in embryogenesis as well as cancer progression3. Cycoplamine has been utilized as a small molecule inducer of stem cell differentiation towards definitive endoderm pancreatic islet cells, as a modulator of cell proliferation, and as an anticancer drug4-6.

Stemgent and the Stemolecule brand name are trademarks of REPROCELL Inc., Japan.
Product Name: Stemolecule Cyclopamine
Catalog Number: 04-0022
Size: 2 mg
Alternate Name(s): (3S,3'R,3'aS,6'S,6aS,6bS,7'aR,9R,11aS,11bR)-3',6',10,11b tetramethylspiro[2,3,4,6,6a,6b,7,8,11,11a-decahydro-1H-benzo[a]fluorene-9,2'-3a,4,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-3H-furo[3,2-b]pyridine]-3-ol
Chemical Formula: C27H41NO2
Molecular Weight: 411.62
CAS Number: 4449-51-8
Purity: Greater than 99% by TLC analysis
Formulation: White crystalline solid or clear solid film at bottom of vial
Solubility: For a 10 mM concentrated stock solution of Cyclopamine, reconstitute the compound by adding 485.9 µL of DMSO to the entire contents of the vial. If precipitate is observed, warm the solution to 37 °C for 2 to 5 minutes. For cell culture, the media should be prewarmed prior to adding the reconstituted compound. Note: for most cells, the maximum tolerance to DMSO is less than 0.5%. This molecule is reported to be soluble in DMSO at 100 mM, ethanol at 49 mM, and methanol at 17 mM.
Storage and Stability: Store powder at 4 °C protected from light. Information about the stability of Stemolecules in solution is largely not available. As a general guideline, we recommend that stock solution be freshly made and stored in aliquots at −20 °C. The effect of storage of stock solutions should be verified for each application.
Quality Control: The purity of Cyclopamine was determined by TLC analysis. The accurate mass was determined by mass spectrometry. Cellular toxicity of Cyclopamine was tested on mouse embryonic stem cells.
- Gaffield, W., Incardona, J.P., Kapur, R.P., and Roelink, H. A looking glass perspective: thalidomide and cyclopamine. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 45: 579-588 (1999).
- Chen, J.K., Taipale, J., Cooper, M.K., and Beachy, P.A. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev 16: 2743-2748 (2002).
- Jiang, J., and Hui, C.C. Hedgehog signaling in development and cancer. Dev Cell 15: 801-812 (2008).
- D'Amour, K.A., Bang, A.G., Eliazer, S., Kelly, O.G., Agulnick, A.D., Smart, N.G., Moorman, M.A., Kroon, E., Carpenter, M.K., and Baetge, E.E. Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 24: 1392-1401 (2006).
- Gallo, R., Grieco, F.A., Marselli, L., Ferretti, E., Gulino, A., Marchetti, P., and Dotta, F. Hedgehog signaling during expansion of human pancreatic islet-derived precursors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1150: 43-45 (2008).
- Xu, F.G., Ma, Q.Y., and Wang, Z. Blockade of hedgehog signaling pathway as a therapeutic strategy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 283: 119-124 (2009).
Additional Publications
- Duong TT; Lim J; Vasireddy V; Papp T; Nguyen H; Leo L; Pan J; Zhou S; Chen HI; Bennet J; Mills JA. Comparative AAV-eGFP Transgene Expression Using Vector Serotypes 1–9, 7m8, and 8b in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells, RPEs, and Human and Rat Cortical Neurons. Stem Cells Int:Article ID: 7281912 (2019).
- Pollen AA; Nowakowski TJ; Shuga J; Wang X; Leyrat AA; Lui JH; Li Z; Szpankowski L; Fowler B; Chen P; Ramalingam N; Sun G; Thu M; Norris M; Lebofsky R; Toppani D; Kemp DW; Wong M; Clerkson B; Jones BN; Wu S; Knutsson L; Alvaredo B; Wang J; Weaver LS; May AP; Jones RC; Unger MA; Kriegtein AR. Low-coverage single-cell mRNA sequencing reveals cellular heterogeneity and activated signaling pathways in developing cerebral cortex. Nature Biotechnology 32:1053 (2014),
- Petros TJ; Maurer CW; Anderson SA; Enhanced derivation of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived cortical interneurons by induced expression of Nkx2.1. Stem Cell Research 11:647-656 (2013).