StemAb™ Anti Human Nanog Antibody
RCAB004P-F
Brand: StemAB™
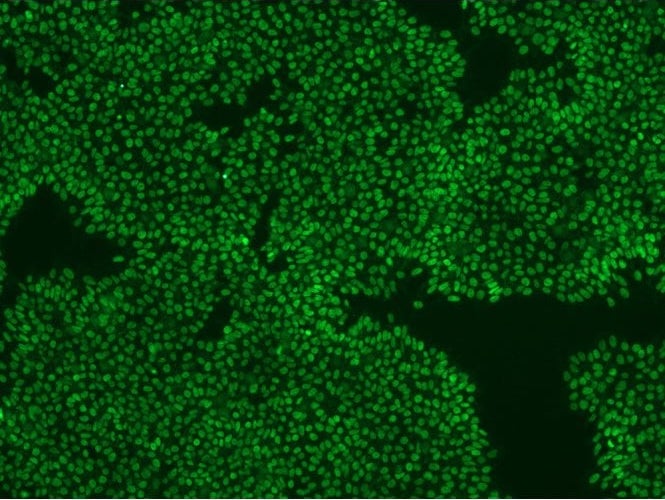
Anti-human IgG antibody to Nanog, a molecular pluripotency marker. Generated in rabbit.
Currency:
| Product name | Catalog number | Pack size | Price | Price (USD) | Price (GBP) | Price (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StemAb™ Anti Human Nanog Antibody | RCAB004P-F | 100 μL | (select above) | $ 449.00 | £ 366.00 | € 428.00 |
Note: prices shown do not include shipping and handling charges.
Product Information
Transcriptional factors, OCT3/4 (POU5F1) and STAT3 function as key regulators in maintaining pluripotency of stem cells. Thus, POU5F1 and STAT3 have been widely used as molecular markers of pluripotential stem cells. Pluripotential cell-specific Nanog gene is a newly identified homeodomain-bearing transcriptional factor. Importantly, Nanog is expressed specific to early embryos and pluripotential stem cells including mouse and human embryonic stem (ES) and embryonic germ (EG) cells. It is a key molecule involved in the signaling pathway for maintaining the capacity for self-renewal and pluripotency, bypassing regulation by the STAT3 pathway. Therefore, Nanog is one of the molecular markers suitable for recognizing the undifferentiated state of stem cells in the mouse and human.
StemAb brand name is the property of REPROCELL Inc., Japan.
Product Name: StemAb Anti-Human Nanog Antibody
Catalog Number: RCAB004P-F
Purity: Immunogen affinity purified
Storage and Stability: Store at 4 °C (short term), −20 °C or −80 °C (long term), stable for 3 years when stored as directed.
Quality Control
- Host: Rabbit
- Immunogen: Human Nanog peptide
- Clonality: Polyclonal
- Purity: Immunogen affinity purified
- Concentration: 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage Buffer: PBS (incl. 0.1% sodium azide)
Notice To Purchaser: This product is for research use only, not for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. It is not allowed to sell this product to a third party or use it for commercial purposes without permission from REPROCELL.
Concentration: 0.2 mg/mL
Immunogen: Human Nanog peptide
Clone: Polyclonal
- Völkner C; Liedtke M; Petters J; Huth K; Knuebel G; Escobar HM; Bullerdiek J; Lukas J; Hermann A; Frech MH. Generation of an iPSC line (AKOSi006-A) from fibroblasts of a NPC1 patient, carrying the homozygous mutation p.I1061T (c.3182 T > C) and a control iPSC line (AKOSi007-A) using a non-integrating Sendai virus system. Stem Cell Res 49:102056 (2020).
- Lee G;Kim H; Park JY; Kim G; Han J; Chung S; Yang JH;' Jeon JS; Woo D-H; Han C; Kim SK; Park H-J; Kim H-H. Generation of uniform liver spheroids from human pluripotent stem cells for imaging-based drug toxicity analysis. Biomaterials in Press://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120529 (2020).
- Peron C; Mauceri R; Cabassi T; Segnali A; Maresca A; Iannielli A; Rizzo A; Sciacca FL; Carelli V; Tiranti V; . Generation of a human iPSC line, FINCBi001-A, carrying a homoplasmic m.G3460A mutation in MT-ND1 associated with Leber’s Hereditary optic Neuropathy (LHON). Stem Cell Res 48:101939 (2020).
- Chi F. Metabolic Regulation of Preimplantation Mouse Embryo Development. Ph. D. Dissertation, UCLA : (2020).
- Sugawara T; Miura T; Kawasaki T; Umezawa A; Akutsu H. The hsa-miR-302 cluster controls ectodermal differentiation of human pluripotent stem cell via repression of DAZAP2. Regen Therap 15:1-9 (2020).
- Suzuki H; Egawa M; Konda T; Imamura K; Enami T; Tsukita K; Suga M; Shibukawa R; Okanishi Y; Uchiyama T; Inoue H; Takahashi R. Generation of a human induced pluripotent stem cell line derived from a Parkinson's disease patient carrying SNCA Stem Cell Res 45:101822 (2020).
- Arai Y; Takami M; An Y; Matsuo=Takasaki M; Hemmi Y; Wakabayashi T; Inoue J; Noguchi M; Nakamura Y; Sugimoto K; Takemura T; Okita K; Osafune K; Takasato M; Hayata T; Hayashi Y. Generation of two human induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from two juvenile nephronophthisis patients with NPHP1 deletion. Stem Cell Res 45:101815 (2020).
- Wang K; Lin R-Z; Hong X; Ng AH; Lee CN; Neumeyer J; Wang G; Wang X; Ma M; Pu WT; Church GM; Melero-Martin JM. Robust differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into endothelial cells via temporal modulation of ETV2 with modified mRNA. bioRxiv :https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.02.973289 (2020).
- Rodríguez-Traver E; Díaz-Guerra E; Rodríguez C; Arenas F; Orera M; Kulisevsky J; Moratalla R; Vicario C. A collection of three integration-free iPSCs derived from old male and female healthy subjects. Stem Cell Res 42:101553 (2020).
- Terao Y; Kurashina Y; Tohyama S; Fukuma Y; Fukuda K; Fujita J; Takemura K. An effective detachment system for human induced pluripotent stem cells cultured on multilayered cultivation substrates using resonance vibrations. Sci Rep 9:15655 (2019).
- Wang X; Han Y; Wang M; Bo C; Zhang Z; Xu L; Liu W; Wang H. Wnt Signaling Protects against Paclitaxel-Induced Spiral Ganglion Neuron Damage in the Mouse Cochlea In Vitro. Biomed Res Intl 2019:7878906 (2019).
- Inoue Y; Kishida T; Kotani S-I; Taga H; Seki M; Ukimura O; Mazada O. Direct conversion of fibroblasts into urothelial cells that may be recruited to regenerating mucosa of injured urinary bladder. Sci Rep 9:106 (2019).
- Umemura Y; Maki I; Tsuchiya Y; Koike N; Yagata K. Human circadian molecular oscillation development using induced pluripotent stem cells. J Biol Rhythms 34:525 (2019).
- Sekine S-I; Kaneko M; Tanaka M; Ninomiya Y; Kurita H; Inden M; Yamada M; Hayashi Y; Inuzuka T; Mitsui J; Ishiura H; Iwata A; Fujigasaki H; Tamaki H; Tamaki R; Kito S; Taguchi Y; Tanaka K; Atsuta N; Sobue G; Kondo T; Inoue H; Tsuji S; Hozumi I. Functional evaluation of PDGFB-variants in idiopathic basal ganglia calcification, using patient-derived iPS cells. Sci Rep 9:5698 (2019).
- Gagliano O; Luni C; Qui W; Bertin E; TOrchio E; Galvanin S; Urciuolo A; Elvassore N. Microfluidic reprogramming to pluripotency of human somatic cells. Nat. Protocols 14:772-737 (2019).